Guide to Data In Motion in RDA Fabric
RDA Pipelines can exchange data even if they are running at different locations, as long as they all connected to same instance of RDA Fabric.
RDA Fabric uses RDA Streams Using NATS for control path as well as as the default mechanism for data path. Any other streaming approach discussed in section 3.2 can also be used for data path. Multiple streaming approaches may be used at the same time.
1. RDA Streams
- Uses NATS Publish-Subscribe to move the data
- Each Stream name is translated into a NATS Subject.
- Any Stream which is added to list of Persistent Streams it is automatically persisted in Opensearch.
- Each subscriber can use a "group" parameter to identify consumer group. If multiple subscribers use same group name, only one of them will receive that specific batch of data.
- Data can be routed to multiple subscribers by using a different group name for each of the subscribers.
- Stream name
NULL(case-insensitive), implies no data will be written or read from that stream. - RDA Streams do not have to be created in RDAF. First time a data is published or subscribed, streams come into existence.
- List of RDA Streams used by RDA Fabric for it's own operations:
| Stream Name | Description |
|---|---|
| rda_system_feature_usage | RDA Portal and Studio capture all usage metrics by feature. This report is accessible via left side menu Analytics |
| rda_system_deployment_updates | Audit trail of changes to Service Blueprints |
| rda_system_gw_endpoint_metrics | RDA Event Gateway data ingestion metrics by ingestion endpoint |
| rda_system_worker_trace_summary | Pipeline execution statistics by Site, Bots etc. |
| rda_worker_resource_usage | Resource usage metrics published by RDA Workers |
| rda_system_gw_log_archival_updates | Log Archive metrics by RDA Event Gateway |
| rda_system_log_replays | Audit trail of Log Archive replays |
| rda_system_worker_traces | Detailed execution traces for each pipeline, published by RDA Workers |
All the above RDA Streams are also Persistent Streams
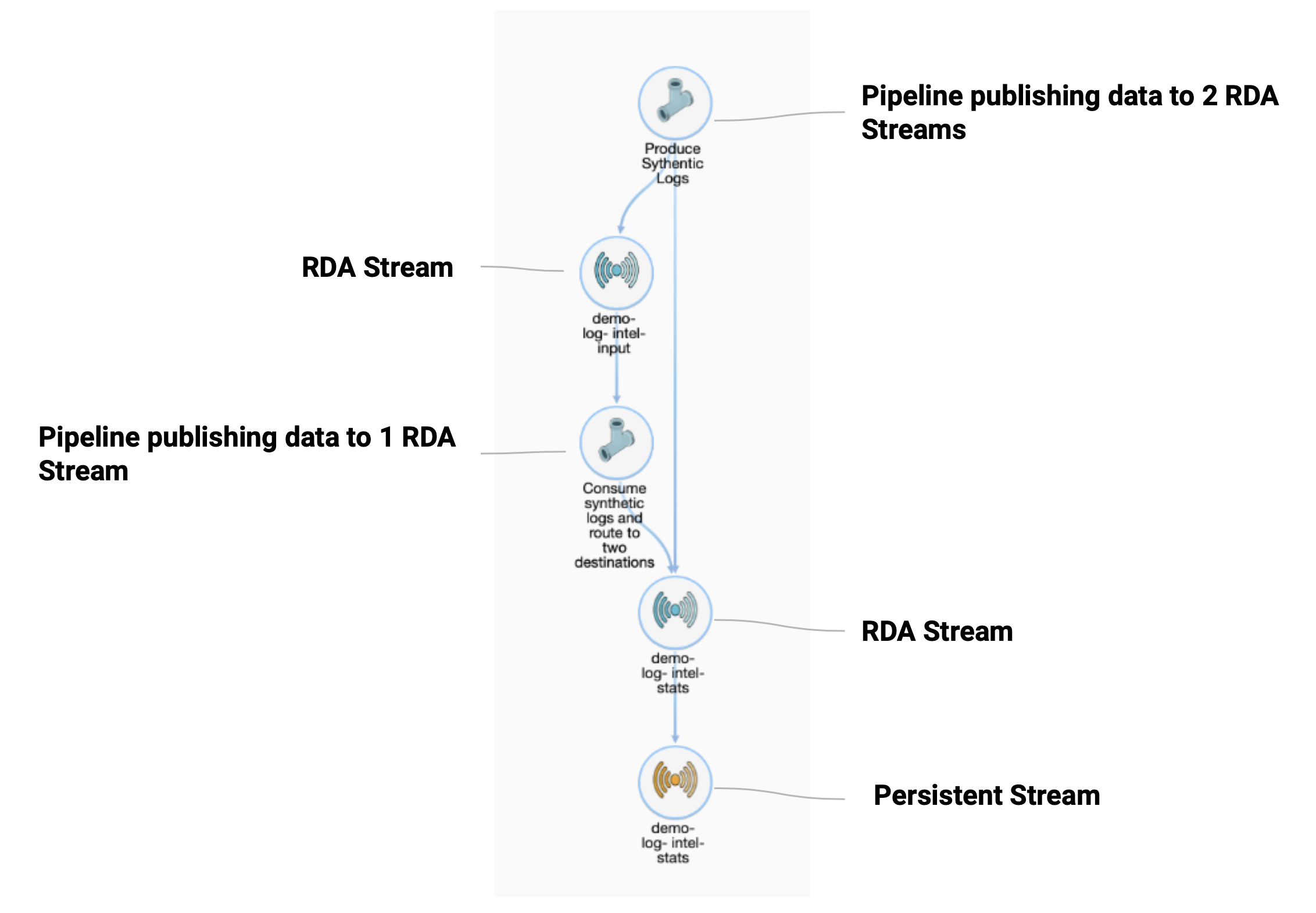
- Example RDA Service Map showing data flow between pipelines using RDA Streams:
Related Bots
Related RDA Client CLI Commands
read-stream Read messages from an RDA stream
read-stream-ack Read messages from an RDA Stream with acknowledgements enabled
write-stream Write data to the specified stream
write-stream-ack Write data to the specified stream with acknowledgement enabled
2. Bots to Manage Data Inflight
This section provides details about various bots to cleanup, re-shape, aggregate, enrich, mask, extract data as it progresses through the pipeline. RDA bots also can be used verify integrity of data to ensure it meets certain criteria.
2.1. Data Cleanup
Data cleanup means getting rid of unnecessary rows & columns, fixing the values, reformatting values on as needed basis.
Following are some of the bots that can be used for cleaning up of the data:
| Bot | Description |
|---|---|
| @dm:dedup | Deduplicates data by using specified column values |
| @dm:dropnull | Drop rows if specified column have null values |
| @dm:map | Map values from one column to another, using optional mapping function and arguments |
| @dm:map-multi-proc | Same as @dm:map, but uses all available CPU core to do parallel processing |
| @dm:eval | Map values using evaluate function. Specify one of more column = 'expression' pairs |
| @dm:eval-multi-proc | Same as @dm:eval, but uses all available CPU core to do parallel processing |
| *dm:filter | Applies a CFXQL filter on input dataframe and returns rows that matches the filter |
| *dm:time-filter | Filter rows using one of the timestamp based column for a specific time range |
| @#dm:filter-using-dict | Applies a CFXQL filters specified in separate dictionary (saved dataset) and returns rows that matches the filters |
| @dm:add-missing-columns | Add columns to dataframe if they are not found. |
| @dm:drop-null-columns | Drop specified columns if they have certain percentage of null values |
| @dm:mergecolumns | Merge columns using 'include' regex and/or 'exclude' regex into a 'to' column |
| @dm:fixcolumns | Fix column names such that they contain only allowed characters |
| @dm:fixnull | Replace null values in a comma separated column list |
| @dm:fixnull-regex | Replace null values in all columns that match the specified regular expression |
| @dm:rename-columns | Rename specified column names using new_column_name = 'old_column_name' format |
| @dm:replace-data | Replace data using regex pattern from list of comma separated columns |
| @dm:selectcolumns | Select columns using 'include' regex and/or 'exclude' regex |
| @dm:to-type | Change data type to str or int or float for specified columns |
| @dm:change-time-format | Change timestamp from one format to another for all specified columns |
2.2 Data Re-shaping
RDA cfxdm extension provides many bots to re-shape inflight data.
Row Based Re-shaping
Following are some of the bots that can do row based re-shaping of inflight data:
| Bot | Description |
|---|---|
| @dm:empty | Creates an empty dataframe. If used as Sink bot, it empties the previous dataframe |
| @dm:addrow | Adds a new row with specified columns and fixed values |
| @dm:head | Keep first n rows of the dataframe and discard the rest |
| @dm:tail | Keep last n rows of the dataframe and discard the rest |
| @dm:sample | Randomly select rows from input. Can be used to select subset of rows or replicate rows randomly to create more rows |
| @dm:sort | Sort rows in ascending or descending order using specified column values |
| @dm:concat | Loads one or more saved datasets, concatenates them and returns a single dataframe |
| @dm:dedup | Deduplicates data by using specified column values |
| @dm:dropnull | Drop rows if specified column have null values |
| @dm:explode | From a specified column value, split it using a seperator, replicate the splitted value into multiple rows. It keeps rest of the columns in-tact |
| @dm:implode | Merge values from different rows into single value for that column |
| @dm:explode-json | From a specified column value, split it as if it a JSON dict or list replicate the splitted value into multiple rows. It keeps rest of the columns in-tact |
| *dm:filter | Applies a CFXQL filter on input dataframe and returns rows that matches the filter |
| *dm:time-filter | Filter rows using one of the timestamp based column for a specific time range |
| @#dm:filter-using-dict | Applies a CFXQL filters specified in separate dictionary (saved dataset) and returns rows that matches the filters |
Column Based Re-shaping
Following are some of the bots that can do column based re-shaping of inflight data:
| Bot | Description |
|---|---|
| @dm:map | Map values from one column to another, using optional mapping function and arguments |
| @dm:map-multi-proc | Same as @dm:map, but uses all available CPU core to do parallel processing |
| @dm:eval | Map values using evaluate function. Specify one of more column = 'expression' pairs |
| @dm:eval-multi-proc | Same as @dm:eval, but uses all available CPU core to do parallel processing |
| @dm:add-missing-columns | Add columns to dataframe if they are not found. |
| @dm:drop-null-columns | Drop specified columns if they have certain percentage of null values |
| @dm:fixcolumns | Fix column names such that they contain only allowed characters |
| @dm:mergecolumns | Merge columns using 'include' regex and/or 'exclude' regex into a 'to' column |
| @dm:rename-columns | Rename specified column names using new_column_name = 'old_column_name' format |
| @dm:selectcolumns | Select columns using 'include' regex and/or 'exclude' regex |
| @dm:transpose | Transposes columns to rows |
2.3 Data Extraction
Following bots can be used to extract data from unstructured logs & events
| Bot | Description |
|---|---|
| @dm:eval | Simple parsing & spitting by a word can be accomplished using this bot |
| @dm:eval-multi-proc | Simple parsing & spitting by a word can be accomplished using this bot |
| @dm:extract | Extract data using Python Named Capturing Groups in Regular Expressions |
| @dm:grok | Extract using Grok Patterns. RDA Supported Grok Patterns |
| @dm:grok-multi-proc | Extract using Grok Patterns. RDA Supported Grok Patterns. Uses multiple processes to accomplish parallel processing of data |
Example Pipeline snippets for Grok Parsing
Playground
Output for the above example
| Column | Value |
|---|---|
| logsource | cfx-rda-worker-vm01 |
| priority | |
| facility | |
| timestamp | Mar 21 03:22:17 |
| program | sshd |
| message | pam_unix(sshd:auth): authentication failure; logname= uid=0 euid=0 tty=ssh ruser= rhost=192.168.101.101 user=macaw |
| pid | 414991 |
| timestamp8601 | |
| meta_grok_message |
2.4 Data Enrichment
Following bots can be used to enrich inflight data with other datasets:
| Bot | Description |
|---|---|
| @dm:enrich | Enrich the input dataframe using a saved dictionary dataset |
| @dm:enrich-using-ip-cidr | Enrich the input dataframe using a saved dictionary dataset. Match IP address in input dataframe with CIDRs specified in the dictionary |
| @dm:enrich-using-ip-cidr-multi-proc | Same as @dm:enrich-using-ip-cidr, but uses all available processors |
| @dm:enrich-using-rule-dict | Enrich using rule based dictionary which contains 'rule' column |
| @dm:dns-ip-to-name | Perform reverse DNS lookup to map IP Addresses to Hostnames on specified columns |
| @dm:dns-name-to-ip | Perform DNS lookup to map Hostnames to IP Addresses on specified columns |
Enrichment using Geo Location Mapping
If the data contains IP Addresses (IPv4 or IPV6), following bot can be used to enrich with geographical location information:
| Bot | Description |
|---|---|
| @geomap:lookup | Enrich the input dataframe using Geo IP mapping |
Playground
Output for the above example
| Column | Value |
|---|---|
| geo_accuracy_radius | 1000.0 |
| geo_autonomous_system_number | 13335.0 |
| geo_autonomous_system_organization | CLOUDFLARENET |
| geo_city_name | Fremont |
| geo_continent_code | |
| geo_continent_name | North America |
| geo_country_iso_code | US |
| geo_country_name | United States |
| geo_is_in_european_union | 0 |
| geo_is_satellite_provider | 0 |
| geo_latitude | 37.562 |
| geo_locale_code | en |
| geo_longitude | -122.0 |
| geo_metro_code | 807.0 |
| geo_network | 104.28.0.0/15 |
| geo_postal_code | 94536 |
| geo_status | found |
| geo_subdivision_1_iso_code | CA |
| geo_subdivision_1_name | California |
| geo_subdivision_2_iso_code | |
| geo_subdivision_2_name | |
| geo_time_zone | America/Los_Angeles |
| ip | 104.28.124.67 |
Enrichment using NLP Techniques
If the data contains natural language text, following NLP techniques can be used to enrich the data:
- Keyword Extraction
- Named Entity Recognition
- Summarization
- Sentiment Analysis
Refer to Natural Language Processing (NLP) in RDA for details on how to accomplish this in RDA.
2.5 Data Integrity
RDA Fabric provides several ways to ensure integrity of the data moving through the fabric.
Following is a brief summary of different ways RDA Pipelines can check for data integrity and possibly take action:
| Integrity Check Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Using Checksum | Using bots @dm:add-checksum and @dm:verify-checksum, it can be ensured that data has not been tampered between an origin and destination. |
| Basic Column Checks | Using bot @dm:check-columns pipeline can look for existence of specific columns and take action on the data. If the intent is to cleanup the data based on amount of nulls in the data, bots @dm:drop-null-columns, @dm:dropnull, @dm:fixnull, @dm:fixnull-regex can be used. |
| Validing Against Schema | RDA can use JSON Schema to validate any data moving through the fabric. Bot @dm:validate-data validates any incoming data against the specified schema. Optionally, RDA Datasets can be bound to a specific JSON Schema, and RDA validates the model everytime dataset is saved or updated. |
| Validating Using Rules Dictionary | Bot @dm:check-integrity uses rules dictionary to validate the data and take an action. Each rule would typically specify expected data types for certain set of columns, nulls allowed or not, range of values allowed for numericals, regex patterns for string data types. Bot @dm:filter-using-dict can be used to drop specific rows based on criteria. Bot @dm:enrich-using-rule-dict can be used to check for very complex data types, relationships and tag each row for further action. |
2.6 Data Masking
RDA provides couple of ways to mask the data. First one using @dm:mask.
Example pipeline
Playground
Output for the pipeline would be:
| Column | Value |
|---|---|
joh************** |
|
| phone_number | *********565 |
| ssn | *******8008 |
Certain types of masking can also be done using @dm:eval. Eval allows more complex types of masking. For example, let us say we want to keep first 3 digits of phone number and last 3 digits intact, we can do this way:
Playground
Output for this pipeline would be
| Column | Value |
|---|---|
***n.doe@xxxxx.yyy |
|
| phone_number | 925*-***-*565 |
| ssn | *****8008 |
2.7 Data Aggregations
RDA cfxdm exention provides many bots that can be used for data aggregations.
Computing Time Series Data Histograms
Historgrams convert timeseries data such as logs & metrics into 'events per time-interval'. Let us use sample-servicenow-incidents dataset and use Service Now incidents as our input dataset. Let us how count how many tickets been opened by month since Jan 1, 2020. Let
Code Snippet: Histogram
Following snippet does:
- Download data from a URL
- Filter the data to retain incidents opened since Jan 1, 2020. We will just retain
sys_created_oncolumn for this purpose - Use @dm:hist bot to compite histogram
- Change the timestamp format for
sys_created_onto show year & month only.
Playground
Output:
| sys_created_on | count |
|---|---|
| 2020-06 | 1 |
| 2020-07 | 0 |
| 2020-08 | 0 |
| 2020-09 | 0 |
| 2020-10 | 0 |
| 2020-11 | 16 |
| 2020-12 | 15 |
| 2021-01 | 0 |
| 2021-02 | 9 |
Computing Time Series Data Histograms with GroupBy
Instead of counting number of tickets opened by month, let us count number tickets opened by month but grouped by priority of the incident. We will use the bot @dm:hist-groupby
Code Snippet: Histogram with GroupBy
Playground
Outpuut:
| sys_created_on | count | priority |
|---|---|---|
| 2020-11 | 10 | 1 - Critical |
| 2020-12 | 0 | 1 - Critical |
| 2021-01 | 5 | 1 - Critical |
| 2020-11 | 3 | 2 - High |
| 2020-12 | 0 | 2 - High |
| 2021-01 | 1 | 2 - High |
| 2020-11 | 4 | 3 - Moderate |
| 2020-12 | 0 | 3 - Moderate |
| 2021-01 | 2 | 3 - Moderate |
| 2020-12 | 2 | 4 - Low |
| 2020-06 | 1 | 5 - Planning |
| 2020-07 | 0 | 5 - Planning |
| 2020-08 | 0 | 5 - Planning |
| 2020-09 | 0 | 5 - Planning |
| 2020-10 | 0 | 5 - Planning |
| 2020-11 | 3 | 5 - Planning |
| 2020-12 | 9 | 5 - Planning |
| 2021-01 | 0 | 5 - Planning |
| 2021-02 | 1 | 5 - Planning |