Persistent Streams
1. RDAF Platform's persistent streams
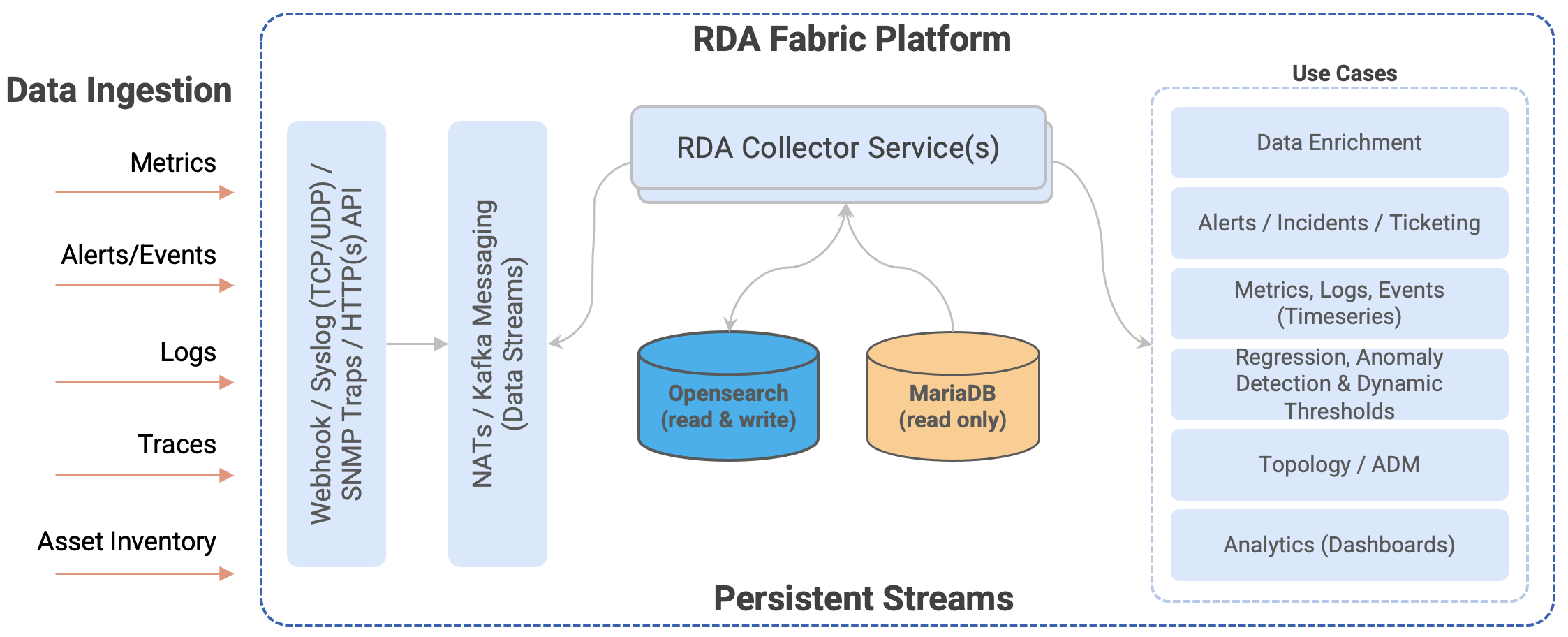
RDAF supports ingesting, processing, consuming data at scale for different use cases such as AIOps, Asset Intelligence, Log Intelligence solutions. Additionally, it deliver the processed data to numerous destinations such as Data lakes, Data Warehousing, ITSM, CMDB, Collaboration, Log management tools and more.
It supports streaming the data such as Metrics, Logs, Events, Traces & Asset Inventory which is processed through RDAF's NATs or Kafka messaging service. By default, the streaming data is ingested, processed and consumed through NATs messaging service which holds the data in-memory during the transit, however, if the data need to be protected against system crashes or restarts, RDAF supports writing the streamed data to disk through persistent stream feature. If the in-transit data also need to be protected, Kafka based persistent stream can be used.
Streamed data is persisted in index store (database) which is consumed by many features or usecases. Below are some of the features or usecases (not limited to) which leverages the persistent streams.
- Alerts / Incidents / Ticketing
- Data Enrichment
- Change Events from ITSM
- Metrics, Logs, Events (Timeseries)
- Asset Inventory and Topology
- Regression, Anomaly Detection & Dynamic Thresholds
- Analytics (Dashboards)
- Others (Custom Usecases)
Persistent streams can be managed through rdac CLI or through RDAF UI portal. By default, RDAF's applications such as OIA (AIOps: Operations Intelligence and Analytics) and AIA (Asset Intelligence and Analytics) comes with pre-created persistent streams.
Additional to system provided persistent streams, users can create new persistent streams to ingest any data for analytics or for any user's specific custom use cases.
Warning
Please do not modify or delete system provided persistent streams. Contact CloudFabrix technical support for any assistance (support@cloudfabrix.com) around system provided ones.
2. Manage persistent stream
Persistent streams can be managed through RDAF UI portal or using rdac CLI.
2.1 Add
Add persistent stream through UI
Login into RDAF UI portal and go to Main Menu --> Configuration --> RDA Administration --> Persistent Streams
Click on Add button to create a new persistent stream
Select Datastore type and Enter persistent stream name.
Tip
When specifying a name for a persistent stream, please use alphanumeric characters. If necessary special characters such as - (dash) or _ (underscore) can be used.
Datastore Types:
- OpenSearch: Opensearch Index store database (support both read and write operations)
- SQL: MariaDB database (support only read operations)
Adding OpenSearch based Persistent Stream:
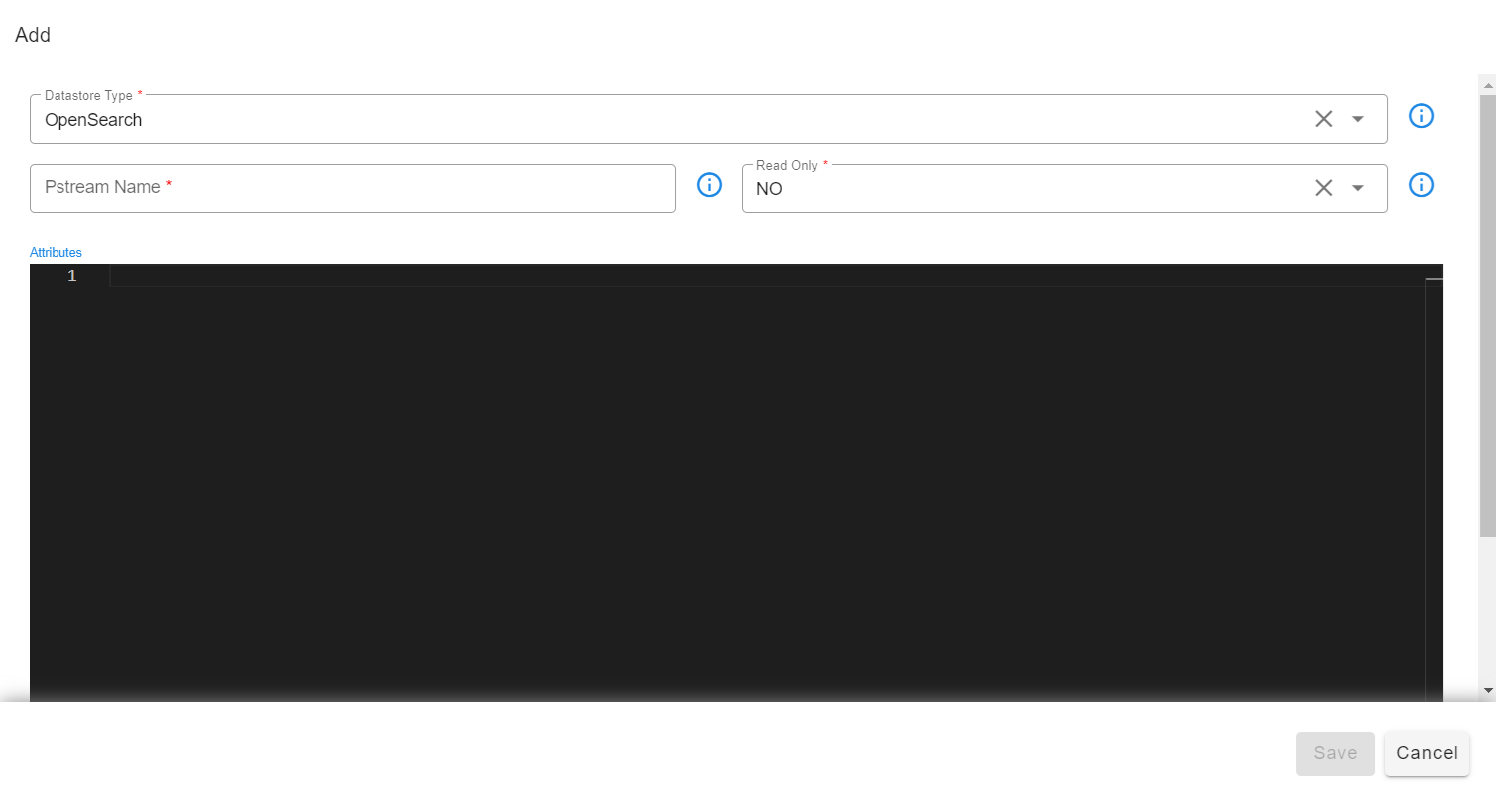
Attributes are settings for persistent streams (optional) and the supported format is in JSON
Below are supported attributes for OpenSearch based persistent streams.
Attribute Name |
Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
retention_days |
no | Specify the data retention time in days (e.g., 7, 10, 15, etc.). When specified, data older than the specified number of days will be permanently deleted. Older data is determined by the timestamp field. Default timestamp field of a persistent stream can be overridden by mapping to another valid timestamp (ISO datetime format) field from the ingested data. |
retention_purge_extra_filter |
no | Specify the CFXQL filter that will be applied to filter the data while deleting older data, based on the retention_days parameter setting. |
timestamp |
no | Map a valid timestamp (in ISO datetime format) field (e.g., created_time, alert_time etc.) from the ingested data to override the default timestamp field. By default, every persistent stream will have a timestamp (in UTC) field that represents the time when the data was ingested. This setting is primarily used for timestamp filter when visualizing the data in Dashboards and for deleting the older data when retention_days is set. |
unique_keys |
no | Specify array of field names (e.g., ["name", "age", "location"] etc.) from the ingested data which will be used to identify uniqueness of each record. Use this option to configure the persistent stream in update mode. By default, persistent stream is configured in append mode. |
search_case_insensitive |
no | This option is used when searching data within the persistent stream. Please specify true or false. When enabled (set to true), the specified text in the filter is searched without case-sensitivity. By default, it is set to true |
default_values |
no | Specify a list of fields for which a default value (e.g., 'Not Available' or 'Not Applicable,' etc.) should be set when their value is empty for some of the records before ingesting into the persistent stream. |
messaging_platform_settings |
no | This setting is only applicable, if you need to use the Kafka messaging service. Configure this setting to specify one or more topics (of RDA Fabric platform or from an external Kafka system) from which to read and ingest the data. By default, persistent streams use the NATs messaging service to read and ingest the data. (Note: When external Kafka system to be used, please configure credential_name parameter to specify the credential name which was created under Configuration --> RDA Integrations) |
auto_expand |
no | Specify array of field names (e.g., ["names", "locations"] etc.) from the ingested data when their value is in JSON format. Extract, flatten and add them as new fields. |
drop_columns |
no | Specify array of field names (e.g., ["tags", "type"] etc.) from the ingested data which need to be dropped before ingesting the data into a persistent stream. |
_settings |
no | Specify index level settings such as number_of_shards, number_of_replicas, refresh_interval etc. Please note that, these settings will be applied only during persistent stream creation time. |
_mappings |
no | Specify index level field mappings to define data types for each field (e.g., double, long, boolean, text, keyword, ip, date etc.). By default, each field's data type is automatically determined based on the data presented in the first record from the ingested data. If the field's data type is not determined, it will be treated as a Text (String). Please note that, these settings will be applied only during persistent stream creation time. |
Below is an example for persistent stream configuration settings when all of the above mentioned options are used.
Tip
Please note that all of the below listed configuration settings are NOT applicable for every persistent stream. Please configure only the applicable settings based on persistent stream use case requirement.
{
"retention_days": 30,
"retention_purge_extra_filter": "asset_status = 'Purge'",
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"timestamp": "collection_timestamp",
"unique_keys": [
"a_id"
],
"drop_columns": [
"correlationparent"
],
"default_values": {
"a_source_systemname": "Not Available",
"a_status": "Not Available",
"a_severity": "Not Available"
},
"auto_expand": [
"payload"
],
"messaging_platform_settings": {
"platform": "kafka",
"kafka-params": {
"topics": [
"ab12ern1a94mq.ingested-alerts"
],
"auto.offset.reset": "latest",
"consumer_poll_timeout": 1.0,
"batch_max_size": 100,
"batch_max_time_seconds": 2
}
},
"_settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1,
"refresh_interval": "1s"
},
"_mappings": {
"properties": {
"value": {
"type": "double"
},
"employee_name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
Adding SQL based Persistent Stream:
Note
Currently, SQL based persistent streams are supported only using RDA Fabric platform's mariadb database. It supports read-only operations querying the data from the configured database and table. For any assistance around this feature, please contact CloudFabrix technical support (support@cloudfabrix.com)
While adding the SQL based persistent stream, please configure the below.
- Datastore Type: Select SQL
- Database Name: Enter database name from the RDAF platform's database (Note: Only databases that have the tenant id as pre-fix in their name are supported)
- Table Name: Enter database table name or view name.
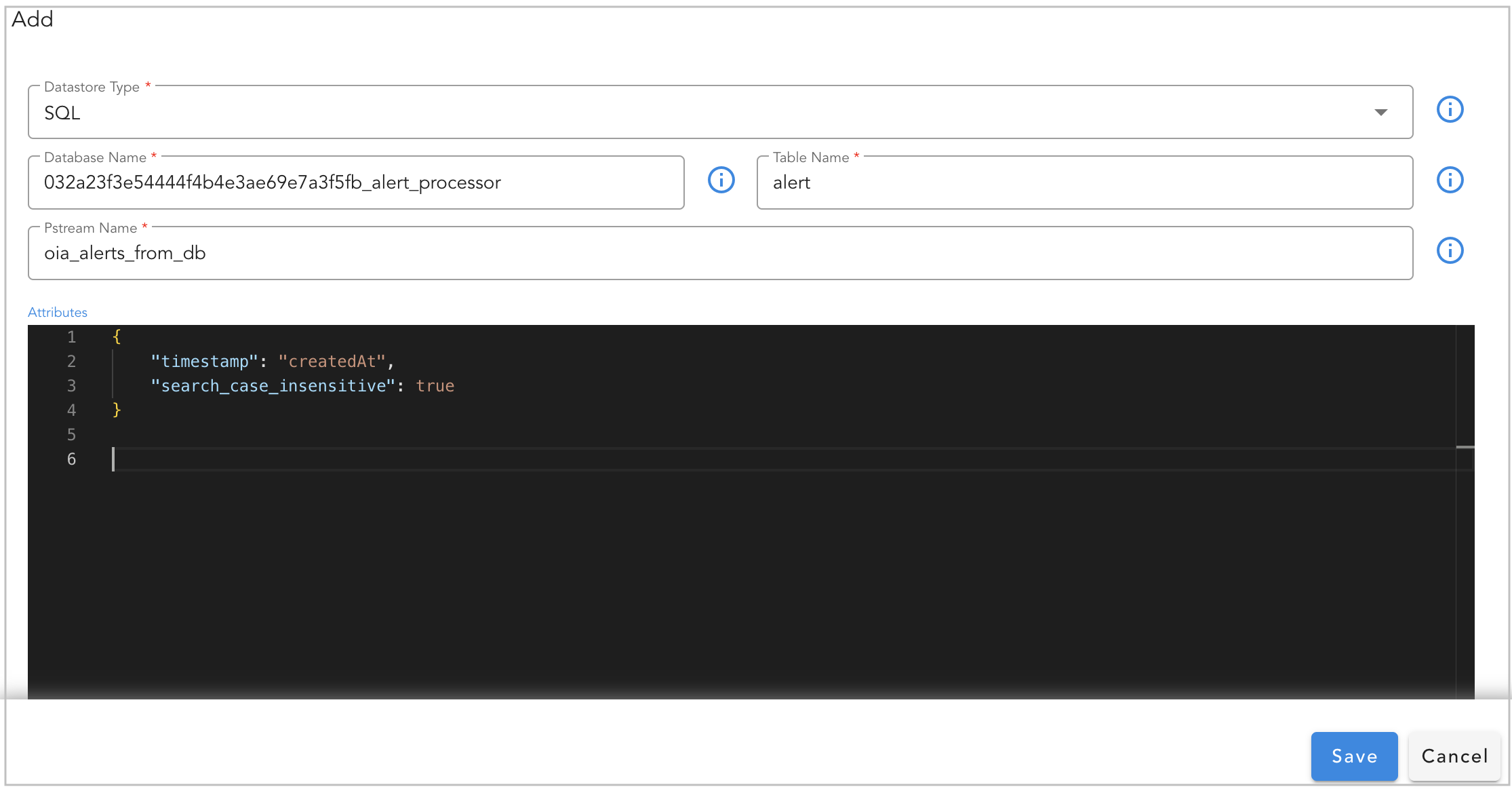
Attributes are settings for persistent streams (optional) and the supported format is in JSON
Below are supported attributes for SQL based persistent streams.
Attribute Name |
Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
timestamp |
no | Map a valid timestamp (in ISO datetime format) field (e.g., created_time, alert_time etc.) from the database table. This setting is primarily used for timestamp filter when visualizing the data in Dashboards. |
2.1.1 Append vs Update
When a persistent stream is created with OpenSearch as a Datastore Type, it operates in either of the below two modes.
- Append: Keep appending every data row as a new record (e.g., Timeseries). This is a default mode.
- Update: Updates the existing data row using the list of filed(s) (as primary key(s)) configured under
unique_keyssetting.
2.1.2 Default value for Field(s)
If a field or fields do not exist in the ingested data record, you can add the default value for the field by configuring the default_values parameter.
In the example below, if the person_name and person_age fields do not exist in the ingested data record, default values of Not Available and 0 will be set for them, respectively.
2.1.3 Computed Field(s)
While ingesting the data, if there's a need to create a new field based on the values of existing fields, the ingest_pipelines setting can be used.
In the following example, the perc_profit and profit fields will be automatically computed and created using the values of the existing sold_price and purchase_price fields, and they will be added to the ingested data record.
For each field, namely perc_profit and profit, configure the `script`` configuration block with the parameters below.
- description: Specify the purpose of this new field
- lang: Set it as painless
- source: Specify the computed formula used to derive the value based on the existing field's value.
- ignore_failure: Set it as true
{
"retention_days": 30,
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"timestamp": "collection_timestamp",
"ingest_pipeline": {
"processors": [
{
"script": {
"description": "Profit Calculator",
"lang": "painless",
"source": "ctx['perc_profit'] = (ctx['sold_price'] - ctx['purchase_price'])*100/(ctx['purchase_price'])",
"ignore_failure": true
}
},
{
"script": {
"description": "Profit",
"lang": "painless",
"source": "ctx['profit'] = ctx['sold_price'] - ctx['purchase_price']",
"ignore_failure": true
}
}
]
}
}
Tip
The ingest_pipelines setting leverages the native capability of the OpenSearch service. It's important to note that, for arithmetic computations, the field's data type should be either long or double.
2.1.4 Multiple Indices Rollover
When managing time series data such as logs or metrics, it's not feasible to write to a single index indefinitely. To ensure good search performance and manage resource usage effectively, data need to be written to an index until it reaches a specified threshold. At that point, a new index is created, and writing continues to the new index.
The following demonstrates how to create a persistent stream with support for automatic rollover across multiple indices. In this example, the rollover occurs when the current write index meets one or more of the following conditions.
-
The current write index was created 7 or more days ago
-
The current write index contains 1,000,000 or more documents
-
The current write index’s size is 100mb or larger
Given the potential for many indices associated with the persistent stream, default behavior is to retrieve field mappings (metadata) from the last 10 indices. If you require information from more indices, you can provide the metadata option as demonstrated below.
{
"retention_days": 30,
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"timestamp": "metric_timestamp",
"multi_indices_rollover": {
"conditions": {
"max_age": "7d",
"max_docs": 1000000,
"max_size": "100mb"
},
"metadata": {
"max_indices": 100
}
}
}
2.1.5 Bounded Dataset
With this feature, the Pstream will be in sync with the selected dataset, i.e., any changes to the data in the dataset automatically get synced to the data in the Pstream. This Pstream is treated as a read-only stream, which means it cannot be written to in any other way.
-
Syncing the data from the dataset to the Pstream will make it easier to use for reporting and other purposes, such as when customers upload their device lists and other information as datasets.
-
This feature also allows multiple Pstreams to be associated with the same dataset, as each Pstream can have additional attributes such as computed columns and enriched information that could differentiate them.
-
If the associated dataset is deleted, the data in the Pstream is not deleted. But if the dataset with the same name is created again, it will automatically sync up with associated Pstreams.
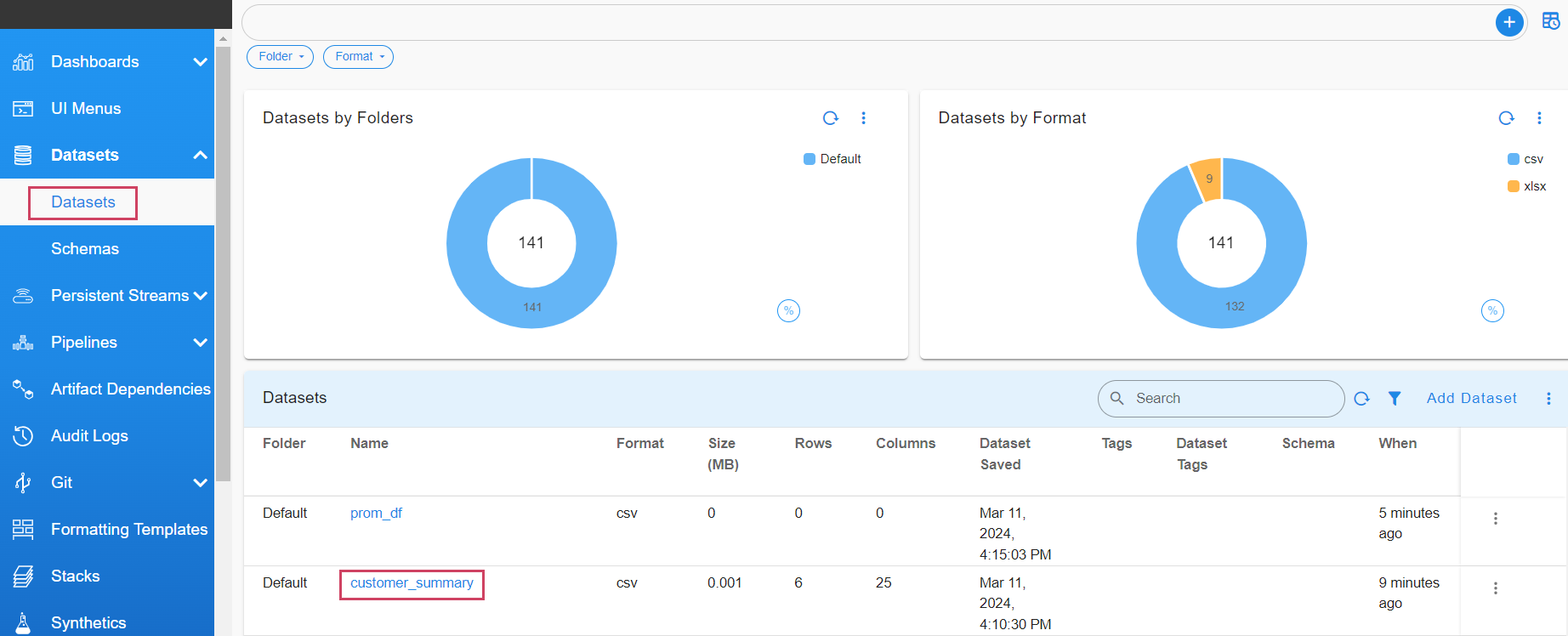
Go to Home -> Configuration -> RDA Administration -> Datasets -> Copy the Dataset Name
- Navigate to Dataset and copy the name of the dataset you wish to map to the Pstream. In this case, customer_summary is used as an example.
- Create a new Pstream associating it to a dataset.
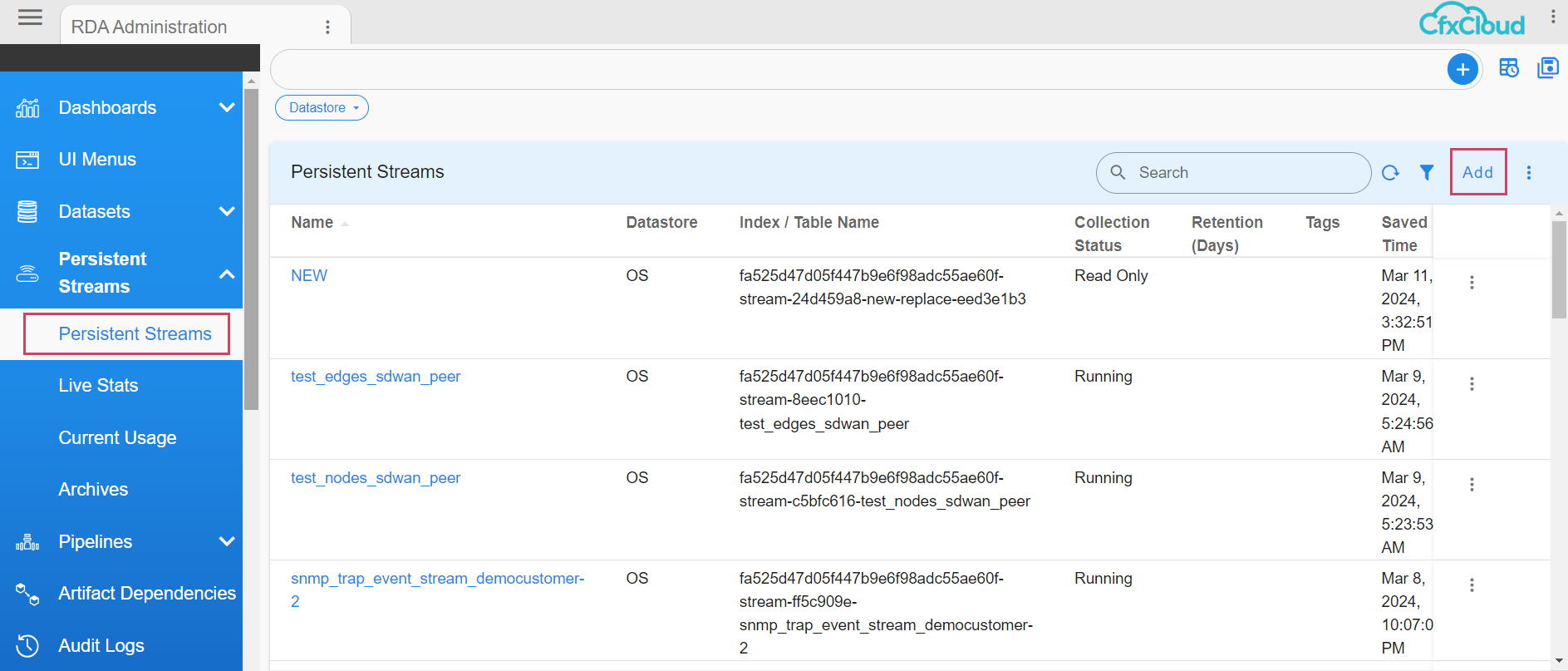
Go to Home -> Configuration -> RDA Administration -> Persistent Streams -> Add
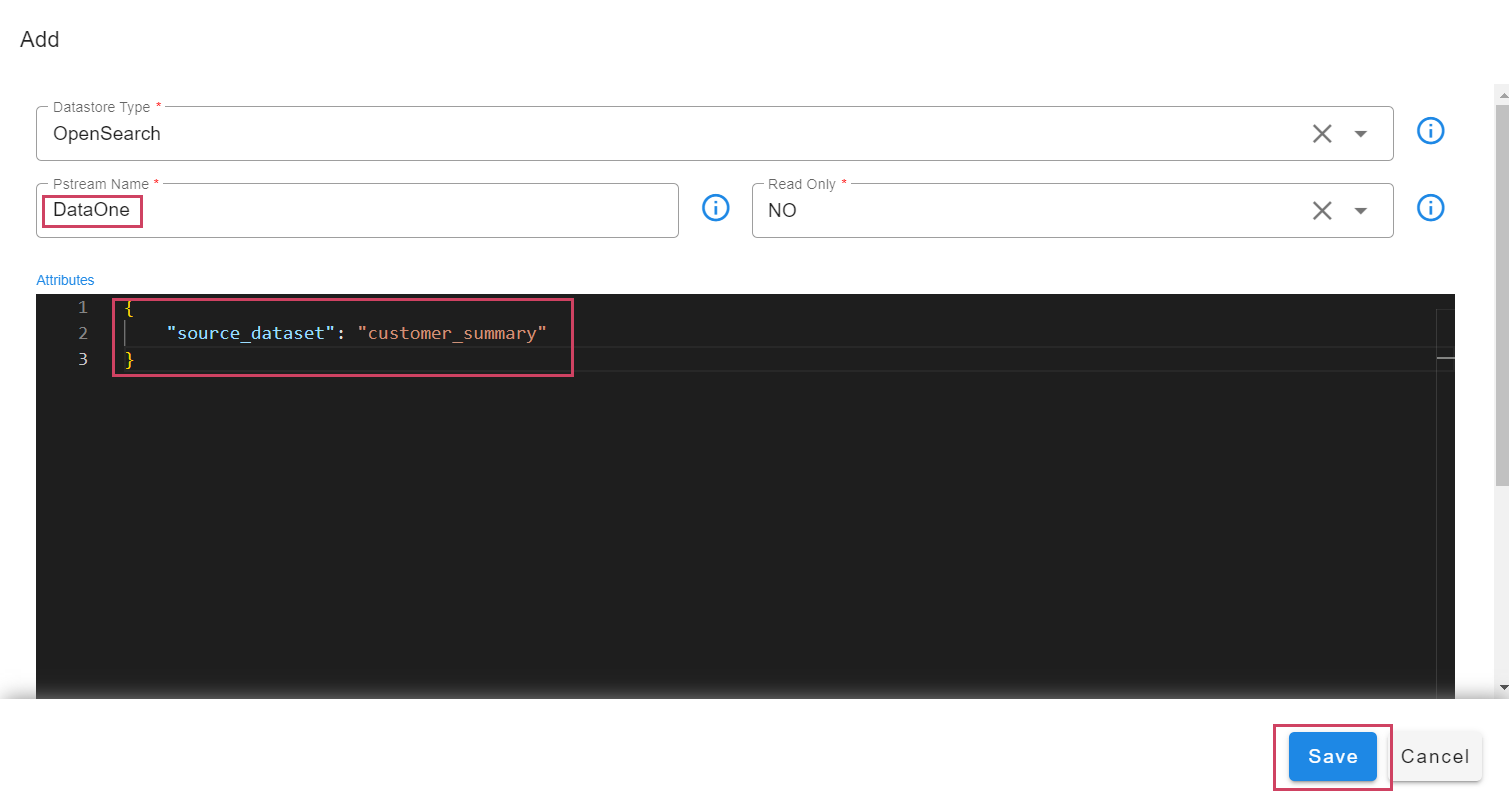
- When adding the Pstream, specify the attribute
source_datasetas shown below.
Warning
The addition of the source_dataset attribute to an already created Pstream is not supported..
Tip
By default, Pstreams are created in append mode unless the unique_keys attribute is defined, which causes the Pstream to write the data in update mode. In the example below, customerName is defined as the unique_key, which uses it as a primary key to maintain a unique record for each customer.
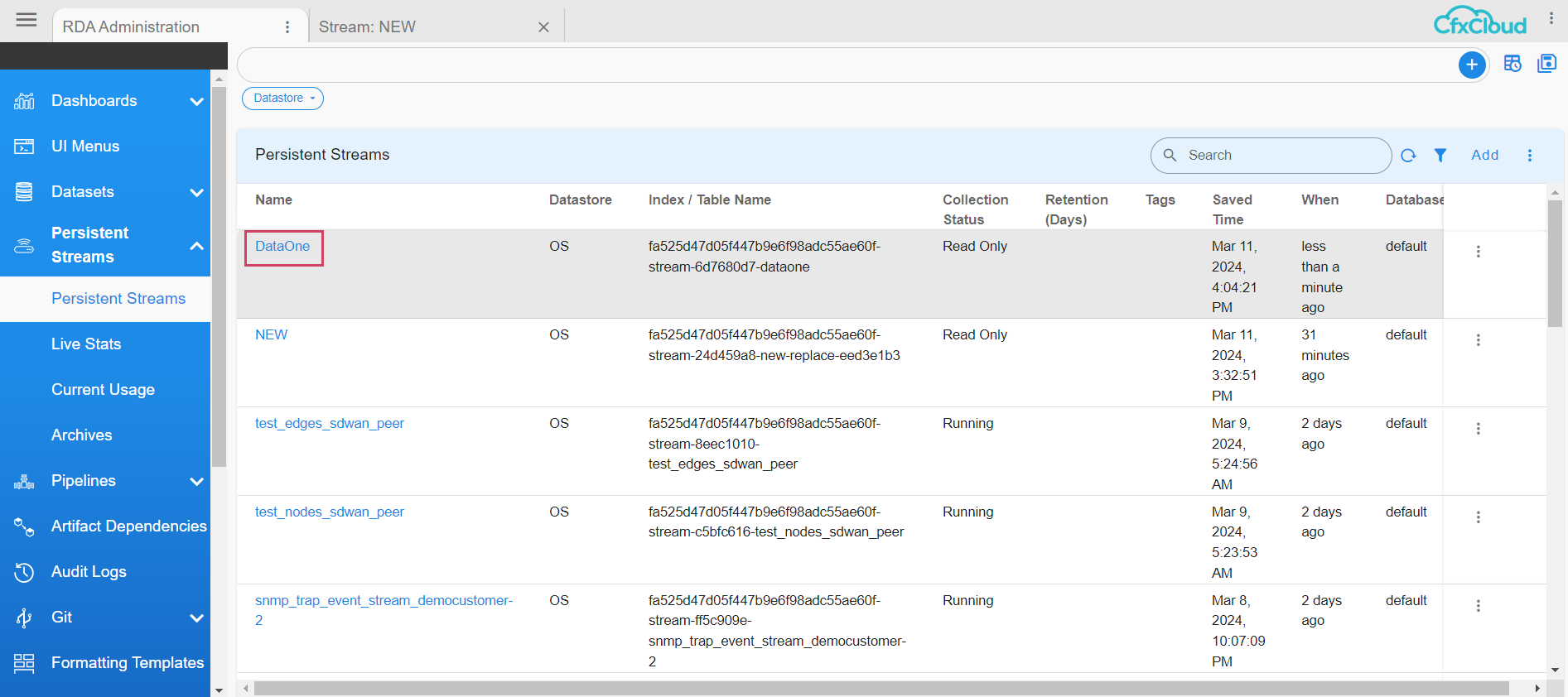
The user can see the Added Pstream that is bound to the Dataset in the below screenshot
The data in the dataset is also visible in the Pstream, as shown below.
2.1.6 Using Kafka Topics
By default, the persistent stream uses streams created out of the NATS messaging service. The RDA Fabric platform also provides Kafka messaging service, which can be used to protect in-transit data against application service outages on the consumption end. During a brief application service outage, Kafka retains unprocessed data on disk (subject to the retention time setting). Once the application service is restored and functional again, the retained data will be processed without any data loss.
In addition to the Kafka messaging service provided by the RDA Fabric platform, external Kafka messaging service is also supported. It can be used within the persistent stream configuration.
Using RDAF Platform's Kafka:
RDAF Platform's Kafka is used by @dn bots (also known as Data Network) to publish and receive events within the platform. However, It can also be used to receive events from external tools.
In the example below, a persistent stream is configured to use a Kafka topic, itsm_snow_incoming_updates, created using the @dn:write-stream bot.
{
"retention_days": 30,
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"timestamp": "collection_timestamp",
"messaging_platform_settings": {
"platform": "kafka",
"kafka-params": {
"topics": [
"itsm_snow_incoming_updates"
],
"auto.offset.reset": "latest",
"consumer_poll_timeout": 1.0,
"batch_max_size": 100,
"batch_max_time_seconds": 2
}
}
}
Tip
In the above example, platform parameter is set to kafka i.e. it uses Data Network feature of the platform to consume the events from the given Kafka topic. (Note: When using the Data Network, the internal naming format for Kafka topics is tenant_id.datanetwork.topic_name (e.g., 032a23f3e54444f4b4e3ae69e7a3f5fb.datanetwork.itsm_snow_incoming_updates))
Using RDAF platform's Kafka topic created for external tools:
In the example below, a persistent stream is configured to utilize a Kafka topic named production_application_events, created by an external tool using the RDAF platform's Kafka credentials for external tools.
- Configure the Persistent Stream with the below settings.
{
"retention_days": 30,
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"timestamp": "collection_timestamp",
"messaging_platform_settings": {
"platform": "kafka-external",
"kafka-params": {
"topics": [
"production_application_events"
],
"auto.offset.reset": "latest",
"consumer_poll_timeout": 1.0,
"batch_max_size": 100,
"batch_max_time_seconds": 2
}
}
}
Tip
In the above example, platform parameter is set to kafka-external and when it is set, the internal naming format for Kafka external topics is tenant_id.external.topic_name (e.g., 032a23f3e54444f4b4e3ae69e7a3f5fb.external.production_application_events)
To publish the events from External tools into RDAF platform, the credentials for RDAF Platform's Kafka, can be found in the /opt/rdaf/rdaf.cfg configuration file. This file is located on the VM where the RDAF deployment CLI was executed to set up and configure the RDAF platform.
[kafka]
datadir = 192.168.125.45/kafka-logs
host = 192.168.125.45
external_user = 032a23f3e54444f4b4e3ae69e7a3f5fb.external
external_password = elJRdWpLVGU2ag==
The externl_password is in base64 encoded format and it need to be decoded to see the actual password using the command echo <external_password> | base64 -d
The Kafka topic for external tools will be automatically created (if it doesn't exist) when the external tool starts publishing events, subject to authentication validation.
Below is the sample configuration settings for external tools to publish the events to RDAF Platform's Kafka.
- Bootstrap Servers: RDAF Platform's Kafka node(s) IPs (comma separated values) with Kafka port 9093 (e.g., 192.168.10.10:9093 or 192.168.10.10:9093,192.168.10.11:9093,192.168.10.12:9093)
- Security Protocol: Set the value as
SASL_SSL - SASL Mechanism: Set the value as
SCRAM-SHA-256 - SASL Username: Enter SASL username created for external tools
- SASL Password: Enter SASL password created for external tools
- SSL CA Certificate: CA certificate from RDAF Platform, ca.pem file can be found under /opt/rdaf/cert/ca/ directory
- Topic name: Kafka topic name. The format should be
tenant_id.external.topic_name(e.g.,032a23f3e54444f4b4e3ae69e7a3f5fb.external.production_application_events) (Note: For tenant id, please go to Main Menu --> Configuration --> RDA Administration --> Network --> For Organization: [tenant_id])
Using External Kafka Cluster:
As a pre-requisite, external Kafka cluster's credentials need to be added under Main Menu --> Configuration --> RDA Integrations --> Credentials --> Click on Add, Select Secret-Type as kafka-v2 and enter the external Kafka cluster settings.
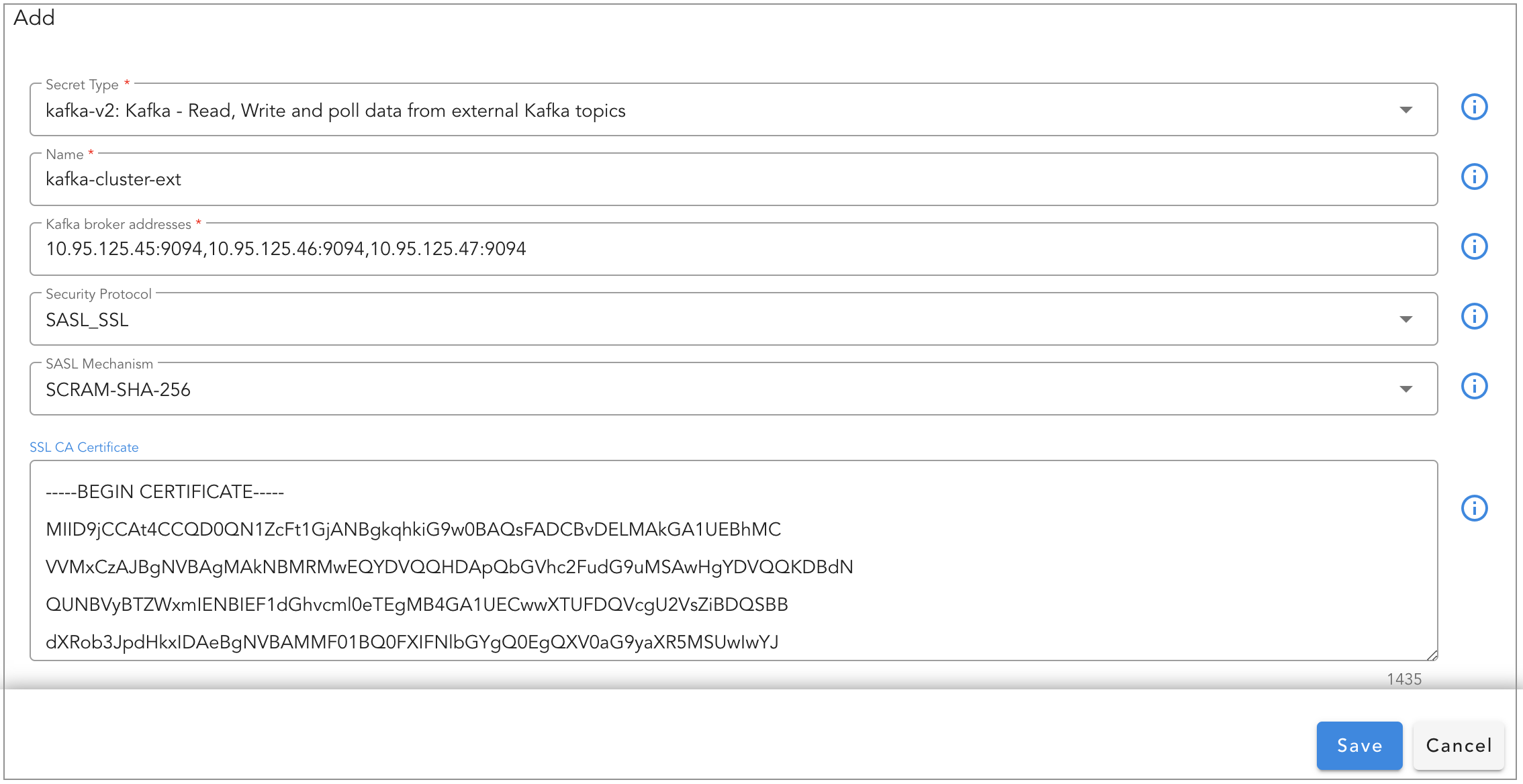
In the example below, a persistent stream is configured to use a external Kafka cluster's topic, metrics_data_lake
Tip
Configure credential_name setting with the credential name of the external Kafka cluster which was created as part of the above pre-requisite step.
{
"retention_days": 30,
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"timestamp": "collection_timestamp",
"messaging_platform_settings": {
"platform": "kafka",
"credential_name": "kafka-cluster-ext",
"kafka-params": {
"topics": [
"metrics_data_lake"
],
"auto.offset.reset": "latest",
"consumer_poll_timeout": 1.0,
"batch_max_size": 100,
"batch_max_time_seconds": 2
}
}
}
2.2 Dashboard
View persistent stream through UI
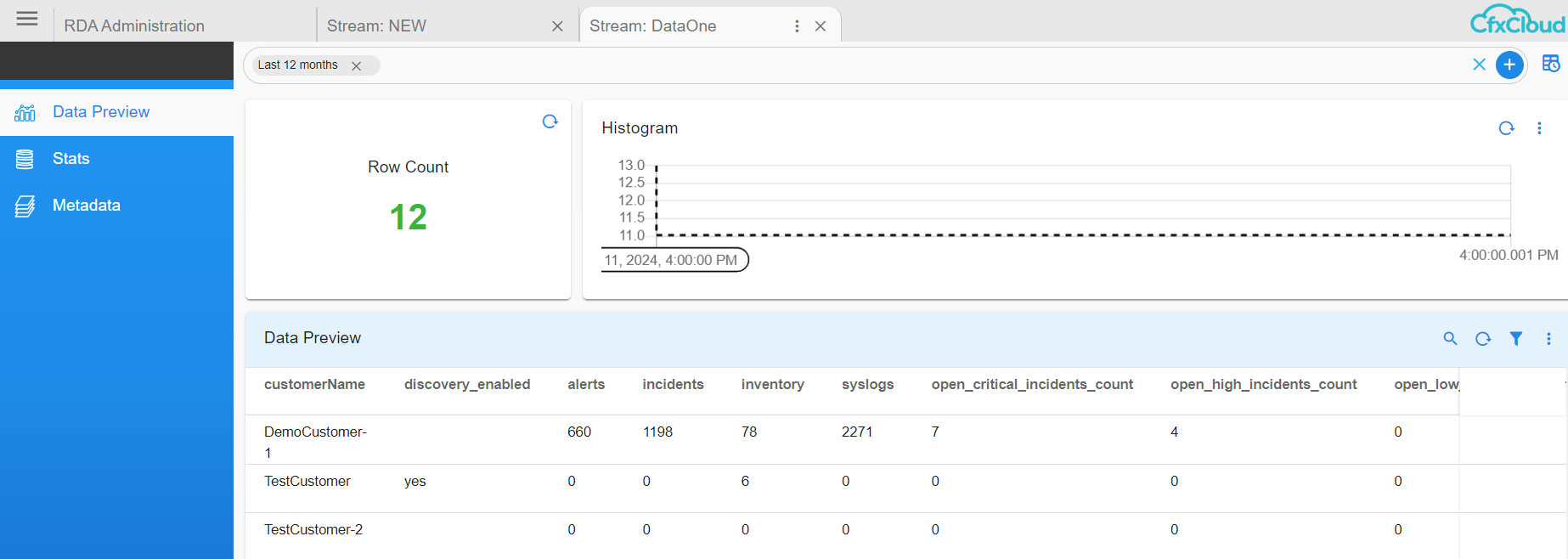
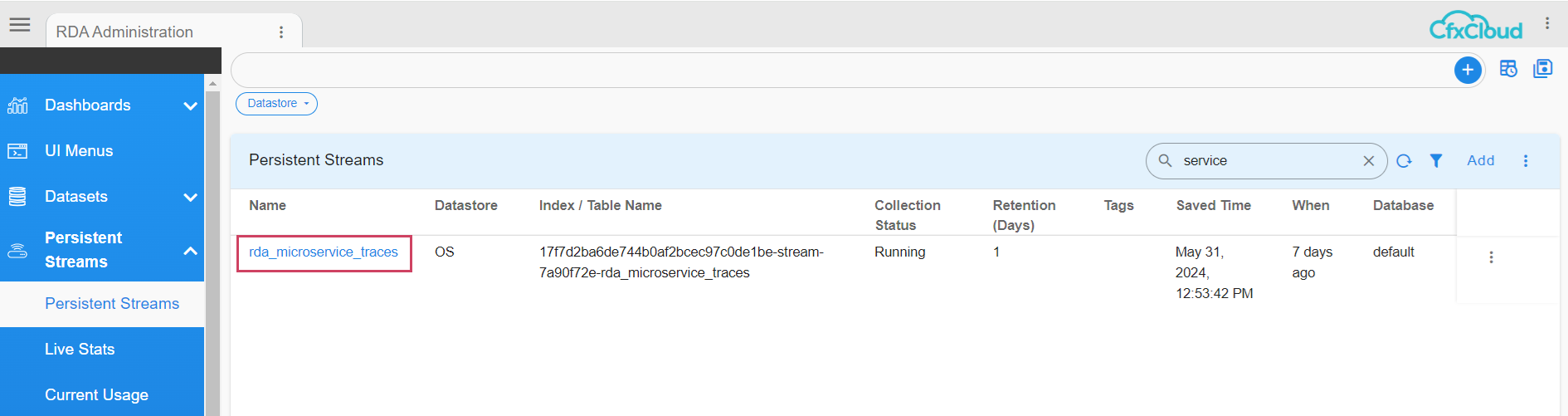
Login into RDAF UI portal and go to Main Menu --> Configuration --> RDA Administration --> Persistent Streams --> Click on the Persistent Stream Here in the below screenshot rda_microservice_traces Persistent Stream is selected to view the data.
Data Preview: In this view, it presents all the ingested data into the persistent stream. It provides a filter bar along with a quick time filter highlighted in the top right side using which data can be filtered to validate the ingested data.
Stats: It provides details about the configuration, usage, and health statistics of the persistent stream, including but not limited to the following:
- status
- docs_count
- index_name
- size_in_bytes
- shards_total
- shards_successful
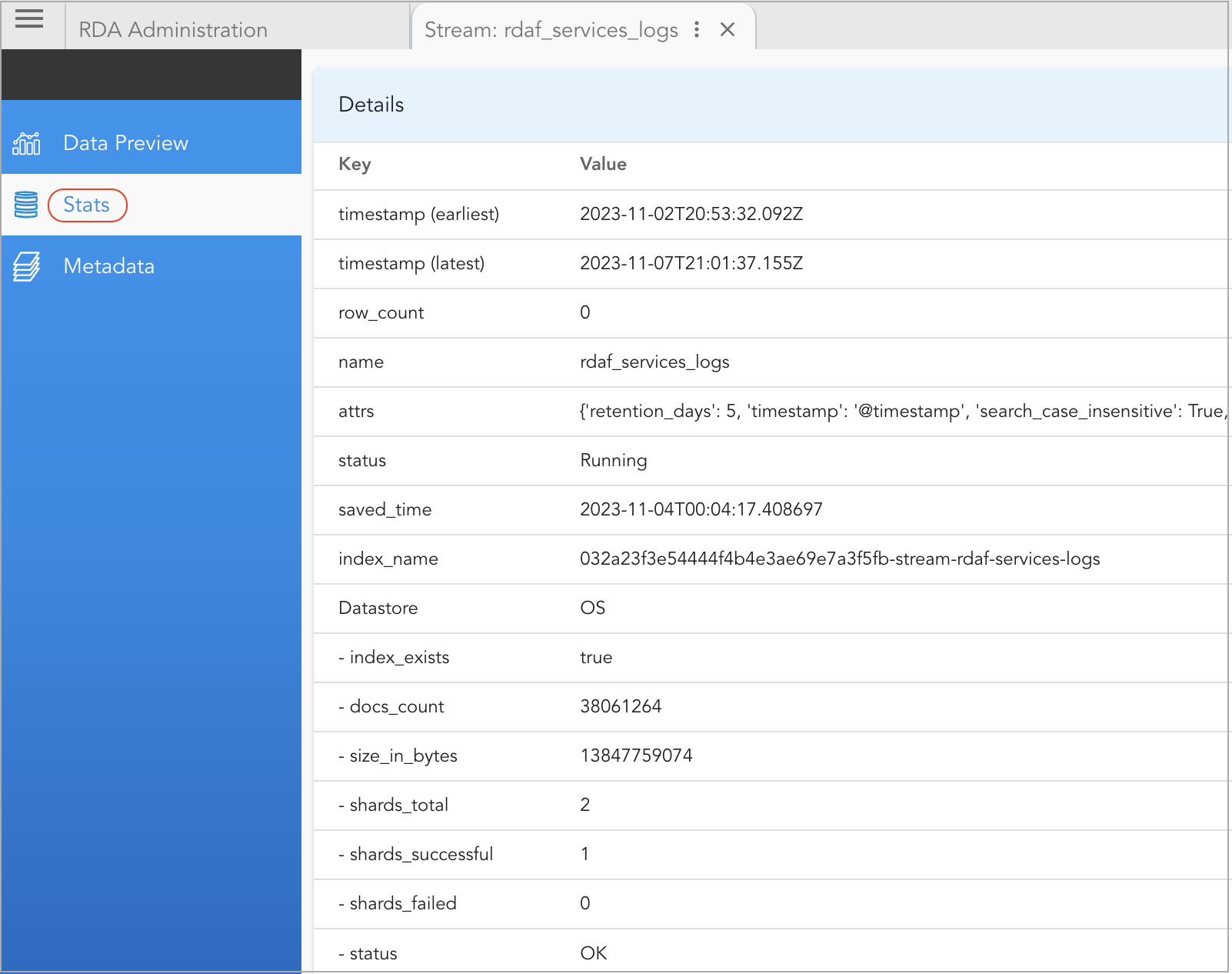
Metadata: It provides details about the schema of the persistent stream.
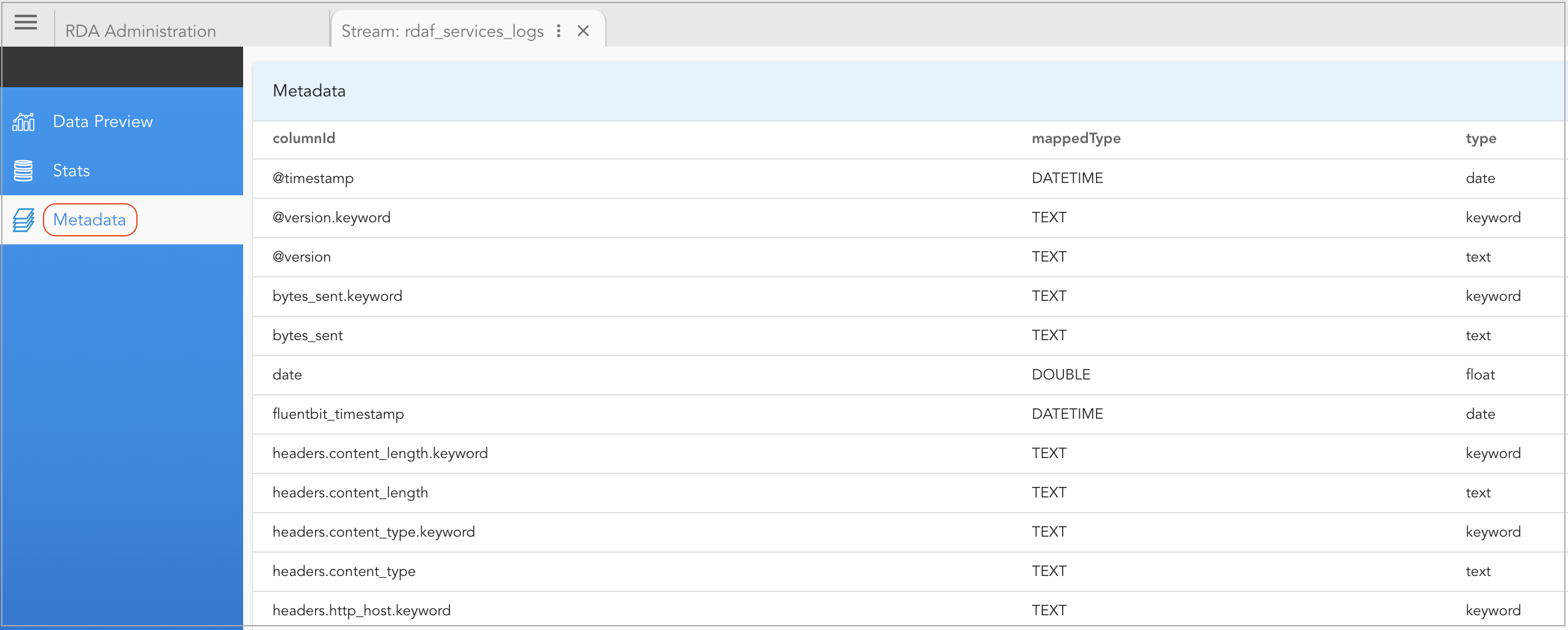
2.3 Edit
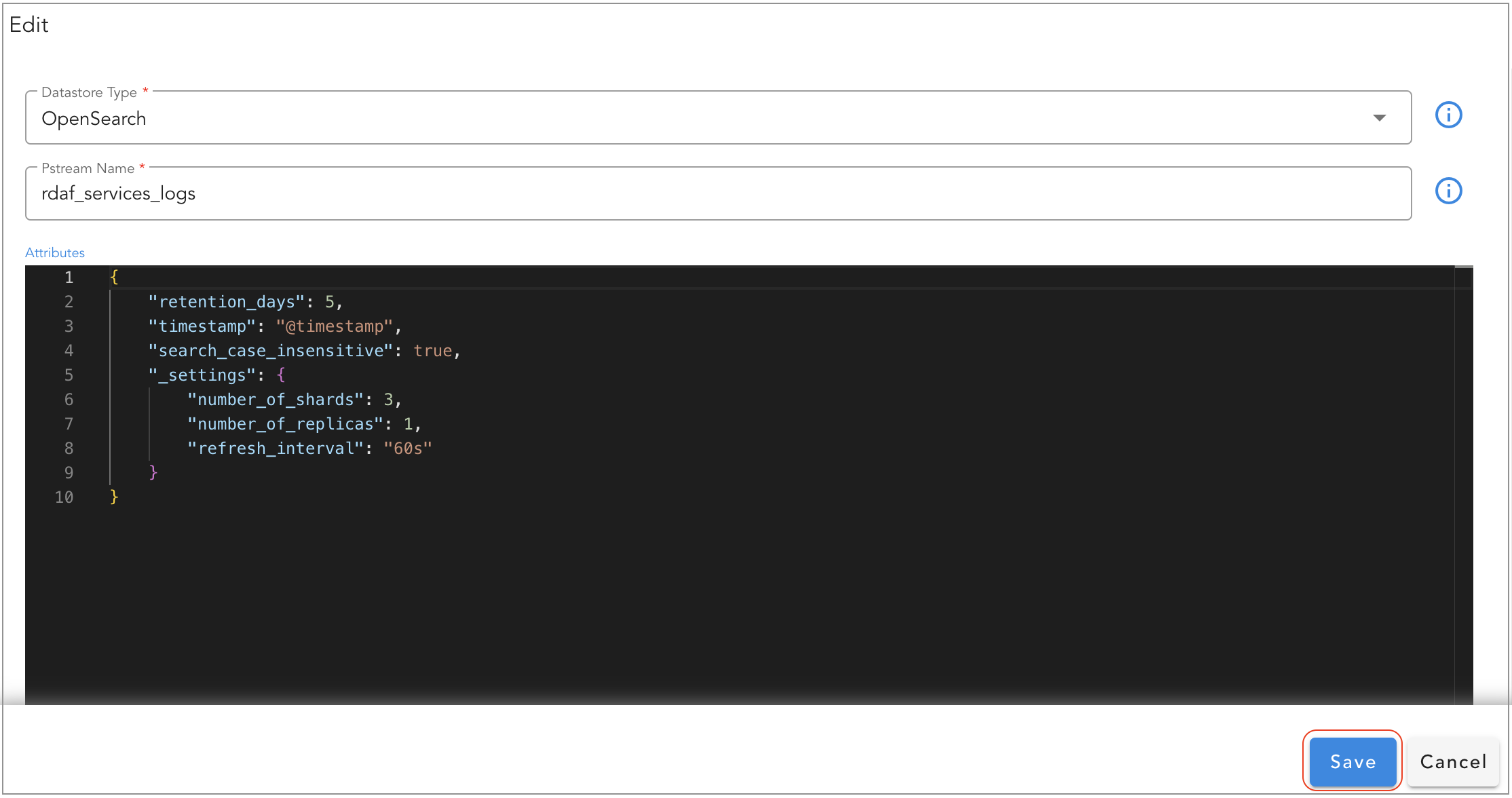
Edit persistent stream through UI
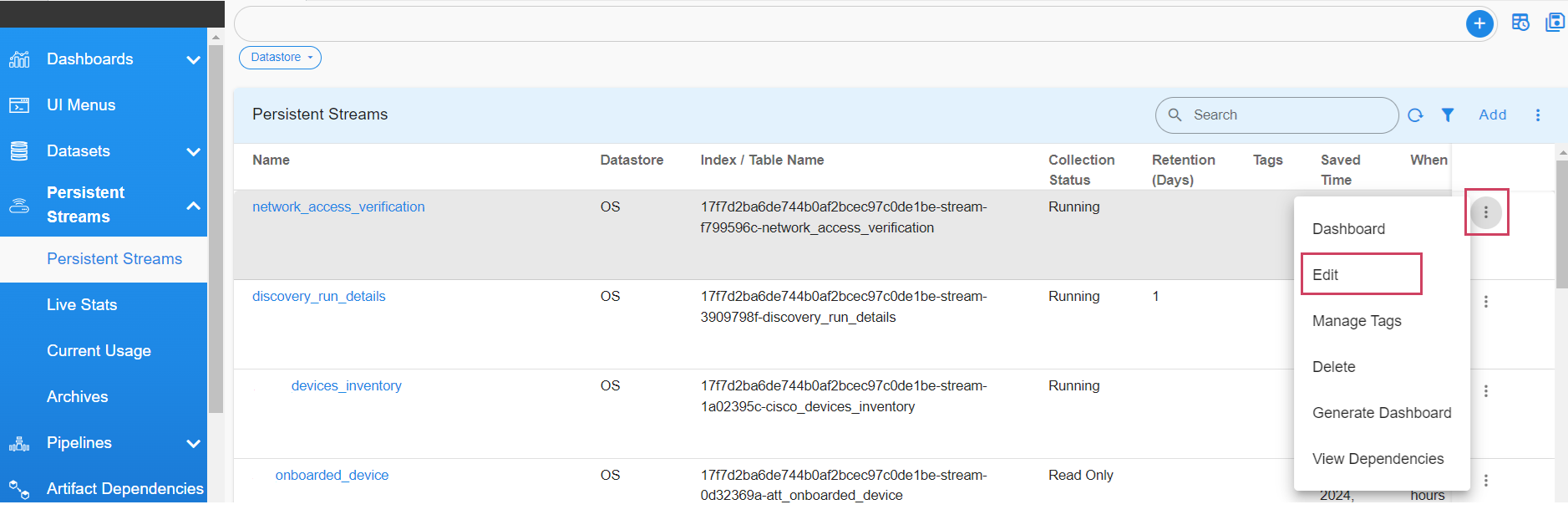
Login into RDAF UI portal and go to Main Menu --> Configuration --> RDA Administration --> Persistent Streams --> Select the Edit Action as shown in the screenshot below
Edit operation will allow to add / modify the settings of the persistent stream.
Note
Please note that, some of the settings are applied only during persistent stream creation time. Please refer attribute settings table for more information.
2.4 Delete
Delete persistent stream through UI
Login into RDAF UI portal and go to Main Menu --> Configuration --> RDA Administration --> Persistent Streams --> From persistent stream menu, select Delete option.
When the persistent stream is deleted without selecting Delete all the data as well option, it will delete only the persistent stream configuration object and it will not delete the index from back-end OpenSearch.
If a new persistent stream is re-created with the same name as before, it will re-use the same index that was not deleted.
To delete the persistent stream along with it's data stored in the Opensearch index, select Delete all the data as well option.
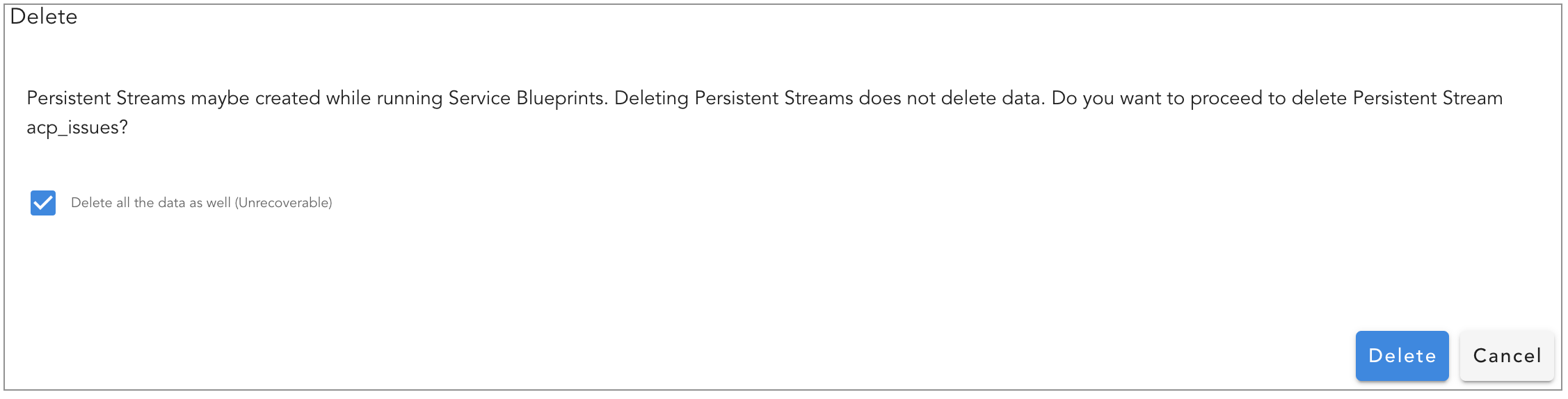
Danger
Deleting a persistent stream with Delete all the data as well option is a non-reversible operation as it will delete the data permanently.
3. Support for Index State Management Based PStreams
Index State Management (ISM) allows user to define policies that automatically handle index rollovers or deletions to fit users use case. These can be automated based on changes in the index age, index size, or number of documents.
Note
It is recommended to use ISM based PStreams for large pstreams used for Metrics, Logs and Events Data (which typically takes up 20GB+ space).
Applying ISM policy to the pstreams which gets build is now supported.
{
"ism": {
"rollover": {
"min_index_age": "1d"
},
"delete": {
"min_index_age": "7d"
},
"index_settings": {
"index.refresh_interval": "60s"
},
"index_mappings": {
"properties": {
"timestamp": {
"type": "date"
},
"metric_value": {
"type": "double"
}
}
}
}
}
- For rollover and delete, user can use
Parameter Name |
Description |
|---|---|
min_index_age |
The minimum age required to roll over the index. Index age is the time between its creation and the present. Supported units are d (days), h (hours), m (minutes). Example: 5d or 7h or 5m |
min_doc_count |
The minimum number of documents required to roll over the index. Ex: 100000 |
min_size |
The minimum size of the total primary shard storage. Example: 20gb or 5mb |
User can also use multiple as follows which means if either condition is met, it will rollover.
Note
Setting multiple for delete is not supported. It will result in ISM policy failure.
Optionally via index_settings and index_mappings User can add/update the default index settings or mappings that exists in the template.
Limitations
The ism option needs to be provided when the pstream is first created. Changing non-SM to ISM based pstream and vice versa is not supported.
retention_days option is ignored for ism policy based pstreams.
It is currently only supported via UI i.e. it is not supported via RDAC.