Kubernetes Cluster
Kubernetes is a portable, extensible, open source orchestration platform for managing containerized workloads and services, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. CloudFabrix's RDA supports integrating with Kubernetes cluster through it's CLI interface (kubectl) over SSH or HTTP API interface to collect the inventory of Kubernetes resources such as pods, nodes, services, deployments etc.. on-demand or on schedule basis.
1. Prerequisites:
Create a service user account with SSH login privileges to connect to one of the Kubernetes master node (on which kubectl was installed) to collect the inventory data. The user should have privileges to run the below command.
- kubectl get *
Info
If kubectl is enabled only for root user, provide sudo privileges to service user account that was created in the above step.
2. Inventory collection using kubectl over SSH:
On CentOS, RHEL & Ubuntu, edit /etc/sudoers file and add the kubetctl command for the user account that is used for data collection. Below configuration setting restricts the service user account to execute only the kubectl get * commands and does not allow any other administrative commands.
Info
SSH user authentication supports both password and SSH key.
3. Inventory collection using HTTP API:
Follow the below steps to create a service user account with read-only permissions to Kubernetes resources for inventory data collection using Kubernetes HTTP API interface.
Step-1: Create a Namespace for service user account
Step-2: Create a service user account and associate it to the above namespace.Step-3: Create a a role for service user account with below configuration contents and apply the role configuration.
cat > cfx-api-access-role.yml << 'EOF'
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cfx-api-access-role
namespace: cfx-kube-discovery
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
EOF
Step-4: Create a role binding for the service user account with the below configuration contents and apply the role bindings configuration.
cat > cfx-api-access-role-binding.yml << 'EOF'
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cfx-api-access-role-binding
namespace: cfx-kube-discovery
subjects:
- namespace: cfx-kube-discovery
kind: ServiceAccount
name: cfx-api-access
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cfx-api-access-role
EOF
Step-5: Get the secret name for service user account.
Tip
In the latest versions of Kubernetes, secrets and tokens are not generated automatically for service accounts. If you see an empty output to the above command, Please follow the steps below to create a secret and token manually.
Create a secret for API service account cfx-api-access
cat > cfx-api-access-secret.yml << 'EOF'
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: cfx-api-access-secret
namespace: cfx-kube-discovery
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: cfx-api-access
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
EOF
Run the command below to update the cfx-api-access service account with the previously created secret cfx-api-access-secret.
kubectl patch serviceaccount cfx-api-access -p '{"secrets":[{"name":"cfx-api-access-secret"}]}' -n cfx-kube-discovery
Get the secret name for service user account.
Step-6: Get the secret token of service user account and decode it. It shows the HTTP bearer token for service account.
Note
The secret name for the cfx-api-access service account is provided in the output of the command executed in Step 5.
kubectl get secrets cfx-api-access-token-XXXXX -o=jsonpath='{.data.token}' -n cfx-kube-discovery | base64 -d
curl -k https://kube-cluster-ip:6443/api/v1/namespaces -H "Authorization: Bearer <bearer token>" --insecure
4. Adding Kubernetes Cluster as Datasource/Extension in RDA Studio
Kubernetes Cluster or any other datasource/extension's configuration is configured in RDA's user interface. Login into RDA's user interface using a browser.
https://[rda-ip-address]:9998
Info
Default username and password of standalone RDA Studio is rdademo and rdademo1234
Under Notebook, click on CFXDX Python 3 box
In the 'Notebook' command box, type botadmin() and alt (or option) + Enter to open datasource administration menu. Click on 'Add' menu and under Type drop down, select kubernetes-inventory
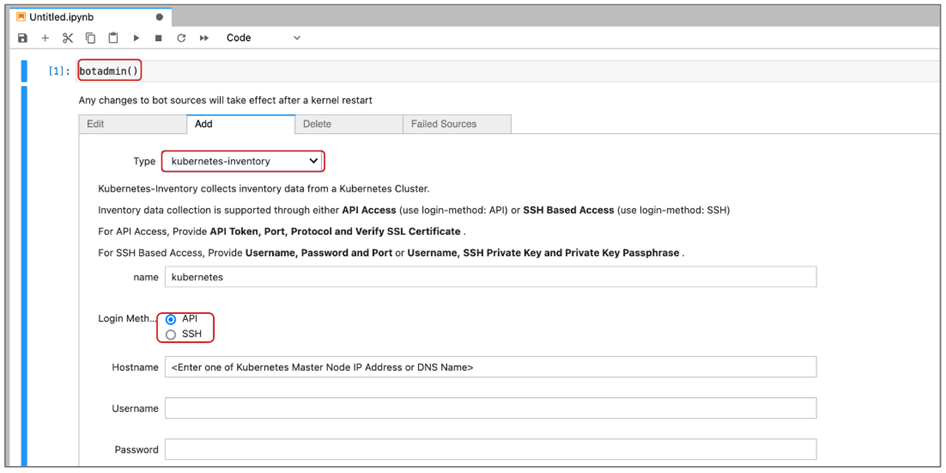
Select API or SSH to access Kubernetes cluster resources for inventory data collection.
Login Method: API (configure the below options)
- Hostname (IP Address or DNS name of Kubernetes cluster)
- Port (HTTP API access port, ex: 6443)
- Protocol (http or https)
- API Token (Service user account's bearer token extracted in Step-6)
- Verify SSL Certificate (Optional)
Login Method: SSH (configure the below options)
- Hostname (IP Address or DNS name of Kubernetes cluster)
- Username (Service user account for SSH access)
- Password (Enter the user's password only when password based authentication is used)
- Private Key Passphrase (Enter the key passphrase only when SSH key based authentication is used)
- SSH Private Key (Enter the SSH RSA key only when SSH key based authentication is used)
- Port (SSH port, default is set to 22)
For the details on Kubernetes cluster inventory data collection bots, refer CloudFabrix RDA Bot Documentation