Guide to Install and Configure RDA Fabric Edge Services
Note
Tags should be updated based on the release, as highlighted in the examples below. Wherever a daily tag appears, it should be replaced with the latest release tag.
1. Install RDA Fabric Edge Services
RDA Worker:
RDA worker nodes are stateless data processing entities that can be installed closed to the source of data generation (ex: on-prem/enterprise/edge sites etc.). Worker nodes execute bots and pipelines and communicate with the RDAF platform that is responsible for scheduling and orchestrating jobs (pipelines) across various worker nodes.
Using worker nodes you can ingest and process/transform data locally without having to send all the data to centralized locations like an analytics platform or data warehouse. Two or more worker nodes in one environment can work as a group for load balancing and scale. RDAF platform can orchestrate data sharing or routing among worker nodes in distributed environments (ex: Worker nodes in edge location exchange data with workers in DC or workers in cloud).
Workers are essentially containerized service nodes and can be installed using Docker-compose or in a Kubernetes environment. Workers are typically installed on VMs that are located on-premises / cloud / edge environments.
RDA Event Gateway:
RDA Event Gateway is a type of RDA Agent that can send streaming data to the RDA Fabric platform. If user wants to send logs/events in real-time to the RDAF platform, users can install Event Gateway in their local environment and configure event sources to send data to Event Gateway.
Similar to RDA worker nodes, event gateways are also containerized services and can be installed using Docker-compose or in a Kubernetes environment. RDA event gateways are typically installed on VMs that are located on-premises / cloud / edge environments.
-
Log Sources: For instance, to send syslogs from your Linux servers to the RDA platform, you can install Event Gateway and configure rsyslog on your Linux servers to send data to Event Gateway, which in turn can send data to the RDAF platform.
-
Existing Log Shippers: Users can also use existing log shippers like Splunk Universal Forwarder, Elasticsearch beats, Fluentd, rsyslog, syslog-ng, etc. to route / send data to Event Gateway.
-
Endpoints: Event Gateway supports endpoints and each endpoint is configured to send data to a stream on RDAF platform. For example, you can configure an endpoint with a port and protocol/type (ex: TCP/syslog) and all syslog sources can send data to that endpoint.
RDA Edge Collector :
RDA Edge Collector is a type of RDA agent that can discover and collect IT asset data in an agentless manner and send the collected data to the RDA Fabric platform. Edge Collector agent is primarily used to discover the IT assets (i.e. Servers, Switches, Routers, Firewall, Load Balancers, Storage Arrays etc.) that provide inventory data over SNMP and SSH protocols.
Similar to RDA worker & event gateway, edge collectors are also containerized services and can be installed using Docker-compose or in a Kubernetes environment. RDA edge collectors are typically installed on VMs that are located on-premises / cloud / edge environments.
1.1 RDA Worker Installation
Prerequisites:
- Linux OS
- Memory - 8GB
- Disk - 50GB
- Python 3.12 or above
- Docker container runtime environment (18.09.2 or above)
- Docker-compose utility (1.27.x or above)
Installation Steps:
Step-1:
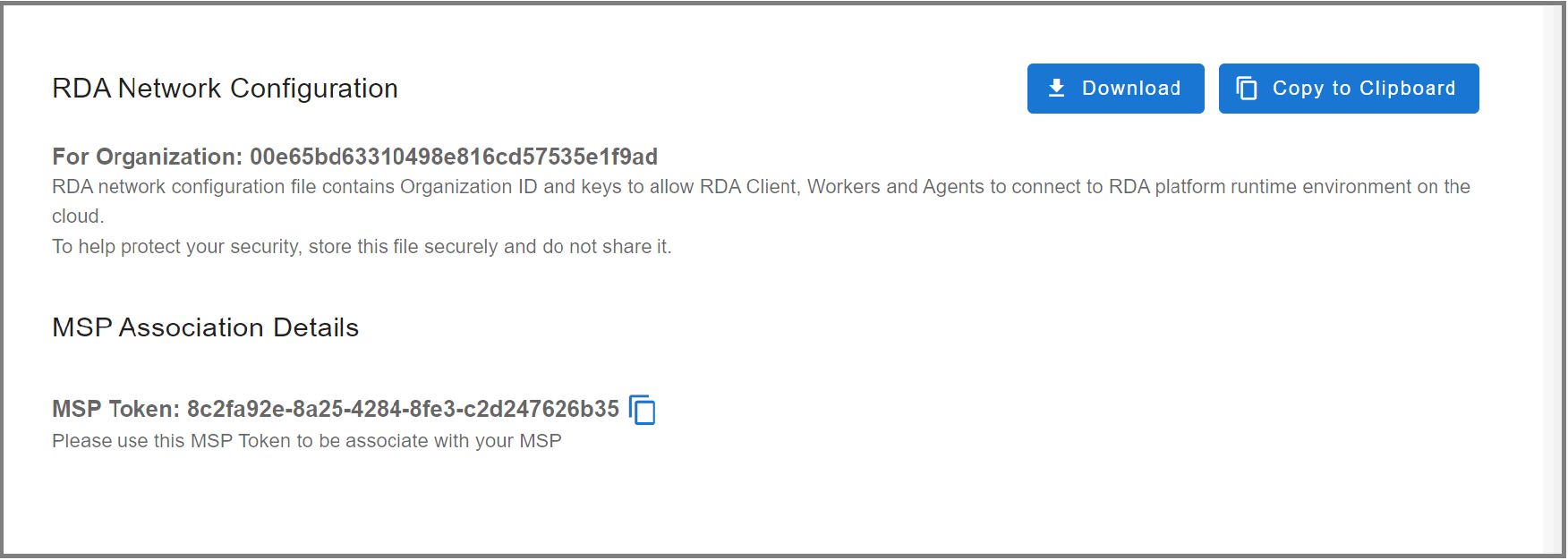
The RDA worker node registers and communicates with the RDAF platform using a configuration file that contains your tenant ID, data fabric access tokens, and object storage credentials.
Download RDA Fabric Configuration from the portal by going to Configuration --> RDA Administration --> Network and copy it to the local filesystem where the worker node is going to be installed.
- Save the file as
rda_network_config.json
- Create the below directory structure
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/network_config
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/worker/config
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/worker/logs
sudo chown -R `id -u`:`id -g` /opt/rdaf
- Copy the downloaded RDA Fabric configuration file as shown below.
- Create common.yml file for RDA Worker to configure logger settings as shown below.
cd /opt/rdaf/worker/config
cat > common.yml << 'EOF'
version: 1
disable_existing_loggers: false
formatters:
standard:
format: "%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(module)s - PID=%(process)s %(message)s"
handlers:
console:
class: logging.StreamHandler
level: INFO
formatter: standard
stream: ext://sys.stdout
file_handler:
class: logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler
level: INFO
formatter: standard
filename: /logs/${pod_type}-${pod_id}.log
maxBytes: 10485760 # 10MB
backupCount: 5
encoding: utf8
root:
level: INFO
handlers: [console, file_handler]
propogate: yes
EOF
Step-2: Docker Login
Run the below command to create and save the docker login session into CloudFabrix's secure docker repository.
Step-3: Create Docker Compose File
Create docker compose configuration file for RDA Worker as shown below.
Tip
Note-1: Optionally change the worker group name (also known as Site) in the docker-compose file by updating the WORKER_GROUP value. In this example, the worker group name is specified as rda_worker_group01
Note-2: Adjust mem_limit and memswap_limit as per the workload requirements. In the below configuration, these parameters are set to 16GB
Note
Tags should be updated based on the release highlighted below. The daily tag that requires updating can be found below.
cd /opt/rdaf/worker
cat > rda-worker-docker-compose.yml <<EOF
version: '3.1'
services:
rda_worker:
image: docker1.cloudfabrix.io:443/external/ubuntu-rda-worker-all:daily
restart: always
network_mode: host
mem_limit: 16G
memswap_limit: 16G
shm_size: 1gb
volumes:
- /opt/rdaf/network_config:/network_config
- /opt/rdaf/worker/config:/loggingConfigs
- /opt/rdaf/worker/logs:/logs
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "25m"
max-file: "5"
environment:
RESOURCE_NAME:
RDA_NETWORK_CONFIG: /network_config/rda_network_config.json
LOGGER_CONFIG_FILE: /loggingConfigs/common.yml
WORKER_GROUP: rda_worker_group01
LABELS: name=rda_worker_01
RDA_SELF_HEALTH_RESTART_AFTER_FAILURES: 3
CAPACITY_FILTER: mem_percent < 95
EOF
Tip
If you are in an HTTP Proxy environment, please configure the HTTP Proxy environment variables as shown below. If there are any target endpoint(s) that don't need to go through the HTTP Proxy, please specify their IP addresses or FQDN names as comma-separated values under the no_proxy and NO_PROXY environment variables.
version: '3.1'
services:
rda_worker:
image: docker1.cloudfabrix.io:443/external/ubuntu-rda-worker-all:daily
restart: always
network_mode: host
mem_limit: 16G
memswap_limit: 16G
shm_size: 1gb
volumes:
- /opt/rdaf/network_config:/network_config
- /opt/rdaf/worker/config:/loggingConfigs
- /opt/rdaf/worker/logs:/logs
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "25m"
max-file: "5"
environment:
RESOURCE_NAME:
RDA_NETWORK_CONFIG: /network_config/rda_network_config.json
LOGGER_CONFIG_FILE: /loggingConfigs/common.yml
WORKER_GROUP: rda_worker_group01
LABELS: name=rda_worker_01
RDA_SELF_HEALTH_RESTART_AFTER_FAILURES: 3
CAPACITY_FILTER: mem_percent < 95
http_proxy: "http://user:password@192.168.122.107:3128"
https_proxy: "http://user:password@192.168.122.107:3128"
no_proxy: "127.0.0.1"
HTTP_PROXY: "http://user:password@192.168.122.107:3128"
HTTPS_PROXY: "http://user:password@192.168.122.107:3128"
NO_PROXY: "127.0.0.1"
Tip
Note-1: RDA worker(s) communicates with RDA Fabric that is running in cloud or on-premise datacenter over ports 4222/TCP & 9443/TCP. Please make sure RDA worker(s) has outbound network access over these network ports. In addition, make sure RDA Fabric is configured to allow inbound network traffic for the same ports to accept the traffic from RDA worker(s).
Note-2: Please verify rda_network_config.json is configured with publicly accessible IP/FQDN of RDA Fabric for NATs and Minio endpoints.
Note-3: If the worker is deployed in proxy environment, please add the required environment proxy variables in /opt/rdaf/deployment-scripts/values.yaml, under the section rda_worker -> env:, instead of making changes to worker.yaml (this is needed only if there are any new changes needed for worker)
Step-4: Bring Up RDA Worker
cd /opt/rdaf/worker
docker-compose -f rda-worker-docker-compose.yml pull
docker-compose -f rda-worker-docker-compose.yml up -d
Note
If Ubuntu version is v22.04.2 LTS or above & Docker Compose version is v2.16.0 or above, Use the following Commands mentioned below
cd /opt/rdaf/worker
docker compose -f rda-worker-docker-compose.yml pull
docker compose -f rda-worker-docker-compose.yml up -d
Check worker node status using docker ps command and ensure that worker is up and running, without any restarts. If you see that the worker is restarting, make sure you copied the RDA network config file to the correct location.
Step-6: Verify RDA Worker in RDA Fabric portal
A newly installed worker will authenticate with the RDA Fabric platform and it will show up in RDA Fabric portal under Fabric Health --> Workers.
Step-7: Verify Worker using RDA Client (rdac) utility
If you have installed RDA Client (rdac) command line utility, you can also verify newly created worker using rdac pods command.
1.2 RDA Event Gateway Installation
Prerequisites:
- Linux OS
- Memory - 8GB
- Disk - 50GB
- Python 3.7.4 or above
- Docker container runtime environment (18.09.2 or above)
- Docker-compose utility (1.27.x or above)
1.2.1 Installation Steps
Step-1:
The RDA event gateway registers and communicates with the RDA Fabirc platform using a configuration file that contains your tenant ID, data fabric access tokens, and object storage credentials.
Download RDA Fabric Configuration from the portal by going to Configuration --> Fabric Configuration --> RDA network configuration and copy it to the local filesystem where the event gateway is going to be installed.
- Save the file as
rda_network_config.json

- Create the below directory structure
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/network_config
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/main
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/snmptrap
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/certs
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/logs
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/log_archive
sudo chown -R `id -u`:`id -g` /opt/rdaf
- Copy the downloaded RDA Fabric configuration file as shown below.
Step-2: Docker Login
Run the below command to create and save the docker login session into CloudFabrix's secure docker repository.
Step-3: Create Docker Compose File
Create docker compose configuration file for RDA event gateway as shown below.
Info
Note: Optionally change the agent group name in the docker-compose file by updating the AGENT_GROUP value. In this example, the agent group name is specified as event_gateway_site01
cd /opt/rdaf/event_gateway
cat > event-gateway-docker-compose.yml <<EOF
version: '3.1'
services:
rda_event_gateway:
image: cfxregistry.cloudfabrix.io/ubuntu-rda-event-gateway:daily
restart: always
network_mode: host
mem_limit: 6G
memswap_limit: 6G
volumes:
- /opt/rdaf/network_config:/network_config
- /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config:/event_gw_config
- /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/certs:/certs
- /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/logs:/logs
- /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/log_archive:/tmp/log_archive
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "25m"
max-file: "5"
environment:
RDA_NETWORK_CONFIG: /network_config/rda_network_config.json
EVENT_GW_MAIN_CONFIG: /event_gw_config/main/main.yml
EVENT_GW_SNMP_TRAP_CONFIG: /event_gw_config/snmptrap/trap_template.json
EVENT_GW_SNMP_TRAP_ALERT_CONFIG: /event_gw_config/snmptrap/trap_to_alert_go.yaml
AGENT_GROUP: event_gateway_site01
EVENT_GATEWAY_CONFIG_DIR: /event_gw_config
LOGGER_CONFIG_FILE: /event_gw_config/main/logging.yml
RDA_SELF_HEALTH_RESTART_AFTER_FAILURES: 3
entrypoint: ["/docker-entry-point.sh"]
EOF
Step-4: Create SNMP Trap Configuration File
Info
Note: Download * trap_to_alert_go.yaml file and copy to /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/snmptrap directory
cd /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/snmptrap/
wget https://macaw-amer.s3.amazonaws.com/releases/rda-edge-services/event_gateway/trap_to_alert_go.yaml
cd /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/snmptrap
cat > trap_template.json <<EOF
{
"1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.4": {
"action": "forward",
"template": {
"message": "Link status changed to up for interface '{{vbValue[3]}}' for device {{ipAddress}}",
"device": "{{ipAddress}}",
"trapOid": "{{trapOid}}",
"snmpVersion": "{{snmpVersion}}",
"timestamp": "{{timestamp}}",
"timestampEpoch": "{{timestampEpoch}}"
}
},
"1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.3": {
"action": "forward",
"template": {
"message": "Link status changed to down for interface '{{vbValue[3]}}' for device {{ipAddress}}",
"device": "{{ipAddress}}",
"trapOid": "{{trapOid}}",
"snmpVersion": "{{snmpVersion}}",
"timestamp": "{{timestamp}}",
"timestampEpoch": "{{timestampEpoch}}"
}
}
}
EOF
Step-5: Bring Up Event Gateway
cd /opt/rdaf/event_gateway
docker-compose -f event-gateway-docker-compose.yml pull
docker-compose -f event-gateway-docker-compose.yml up -d
Step-6: Check event gateway status
Check event gateway service status using docker ps command and ensure that event gateway is up and running, without any restarts. If you see that the event gateway is restarting, make sure you copied the RDA network configuration file to the correct location.
Step-7: Verify RDA Event Gateway in RDA Fabric portal
A newly installed event gateway will authenticate with the RDA Fabric platform and it will show up in RDA Fabric portal under Configuration --> Fabric Components --> Agents --> View Details.
Step-8: Verify RDA Event Gateway using RDA Client (rdac) utility
If you have installed RDA Client (rdac) command line utility, you can also verify newly created event gateway using rdac agents command.
1.2.2 Installation Steps - HA
Nginx Load Balancer Deployment Steps
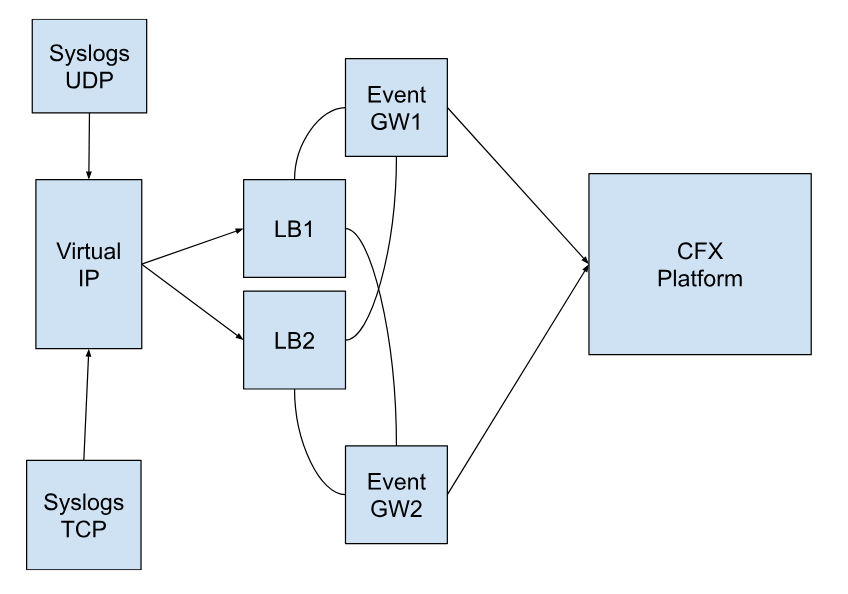
Configuration Diagram for Event GW → Nginx LB → CFX Platform
Prerequisites
1.) Need 2 VMs to configure the Nginx Load Balancer
2.) CFX Event Gateways
- Instructions on How to install Nginx Load Balancer for Event Gateway and Configure Keepalived for LB High Availability (active/passive)
Step-1: Login to the LB VMs and follow the steps on each LB VM
- Create the required folder and file.
worker_rlimit_nofile 1000000;
worker_processes auto;
events {
worker_connections 50000;
}
stream {
upstream rda-eg-udp {
hash $remote_addr consistent;
zone dns_zone 64k;
server 192.168.1.180:514 fail_timeout=300s max_fails=1;
server 192.168.1.63:514 fail_timeout=300s max_fails=1;
}
server {
listen 514;
proxy_pass rda-eg-udp;
proxy_timeout 1s;
proxy_protocol on;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
error_log /var/log/nginx/tcp_514_error.log;
}
server {
listen 514 udp;
proxy_pass rda-eg-udp;
proxy_responses 0;
proxy_timeout 120s;
proxy_protocol on;
proxy_buffer_size 10240k;
error_log /var/log/nginx/udp_error.log;
}
upstream rda-eg-trap-udp {
hash $remote_addr consistent;
zone dns_zone 64k;
server 192.168.1.180:162 fail_timeout=300s max_fails=1;
server 192.168.1.63:162 fail_timeout=300s max_fails=1;
}
server {
listen 162 udp;
proxy_pass rda-eg-trap-udp;
proxy_responses 0;
proxy_timeout 120s;
proxy_protocol on;
proxy_buffer_size 10240k;
error_log /var/log/nginx/udp_trap_error.log;
}
server {
listen 162;
proxy_pass rda-eg-trap-udp;
proxy_timeout 1s;
proxy_protocol on;
proxy_connect_timeout 1s;
error_log /var/log/nginx/tcp_162_error.log;
}
}
http {
server {
listen 9080 default_server;
access_log off;
location /lb-status {
return 200 'OK';
add_header Content-Type text/plain;
}
location /nginx_status {
stub_status;
}
}
}
Note
The lines that are highlighted above presume two event gateways. If a user has more event gateways, add additional lines to the upstream configuration for each upstream mentioned above. At least two is the recommended number.
- Deploy nginx LB using the docker-compose
cat > nginx-docker-compose.yml <<EOF
version: '3'
services:
nginx:
image: nginx:1.25
container_name: nginx
ports:
- "514:514/udp"
- "514:514/tcp"
- "162:162/udp"
- "162:162/tcp"
- "9080:9080/tcp"
volumes:
- ./conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- /opt/rdaf/logs/nginx:/var/log/nginx
restart: always
EOF
- Create
master-keepalived.conffile
global_defs {
script_user root
enable_script_security
}
vrrp_script chk_health {
script "/usr/local/bin/nginx_healthcheck.sh"
interval 2
}
vrrp_instance rdaf_vrrp_ext {
interface ens160
state MASTER
virtual_router_id 11
priority 255
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.102.71/24
}
track_script {
chk_health
}
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1a2b3c4d
}
}
Note
Update/replace the virtual IP in the above file where highlighted as per the environment.
- Copy the file to the path below.
- Create the
nginx_healthcheck.shand copy the file in given pathNginx_healthcheck.sh
#!/bin/bash
HTTP_STATUS=$(curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:9080/lb-status)
if [[ $HTTP_STATUS -ge 200 && $HTTP_STATUS -lt 300 ]]; then
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:514 # dummy TCP request
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:162 # dummy TCP request
exit 0 # Success
else
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:514 # dummy TCP request
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:162 # dummy TCP request
exit 1 # Failure
fi
- copy
nginx_healthcheck.shto/usr/local/bin
- Usage of the script
- start keepalived
- To check the virtual IP in the output, run the below command.
- Configure the firewalls using the below commands.
sudo ufw allow from 224.0.0.18
sudo ufw allow to 224.0.0.18
sudo ufw allow 514/udp
sudo ufw allow 514/tcp
sudo ufw allow 162/udp
sudo ufw allow 162/tcp
sudo ufw allow 9080/tcp
sudo ufw reload
Note
If there are any changes,the necessary ports must be updated accordingly.
- Check if LB is accessible via virtual IP by running the following command
Note
The command above should return as 'OK'
Step-3: Setup keepalived on LB VM 2
- Create
backup-keepalived.conffile.
global_defs {
script_user root
enable_script_security
}
vrrp_script chk_health {
script "/usr/local/bin/nginx_healthcheck.sh"
interval 1
}
vrrp_instance rdaf_vrrp_ext {
interface ens160
state BACKUP
virtual_router_id 11
priority 100
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.102.71/24
}
track_script {
chk_health
}
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1a2b3c4d
}
}
Note
update/replace the highlighted virtual IP in the above file. It should be the same as the previous config that was in LB1
- Copy the file to the path below
- Create the
nginx_healthcheck.shand copy the file in given pathNginx_healthcheck.sh
#!/bin/bash
HTTP_STATUS=$(curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:9080/lb-status)
if [[ $HTTP_STATUS -ge 200 && $HTTP_STATUS -lt 300 ]]; then
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:514 # dummy TCP request
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:162 # dummy TCP request
exit 0 # Success
else
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:514 # dummy TCP request
curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" http://localhost:162 # dummy TCP request
exit 1 # Failure
fi
- copy
nginx_healthcheck.shto/usr/local/bin
- Usage of the script
- start keepalived
- To check the virtual IP in the output, run the below command.
Note
The Virtual IP will not show until LB2 has become active.
- Configure the firewalls using the below commands.
sudo ufw allow from 224.0.0.18
sudo ufw allow to 224.0.0.18
sudo ufw allow 514/udp
sudo ufw allow 514/tcp
sudo ufw allow 162/udp
sudo ufw allow 162/tcp
sudo ufw allow 9080/tcp
sudo ufw reload
Note
If there are any changes,the necessary ports must be updated accordingly.
- Check if LB is accessible via virtual IP by running the following command
Note
The command above should return as 'OK'
Verification Steps
Send events to virtual ip instead of event gateway IP; below is an example that you can refer to
1.2.3 SSL Configuration for endpoints
Run the below command on event gateway to generate self-signed certificate files. Fill in the answers for the below prompts.
- Country Name (2 letter code)
- State or Province Name (full name)
- Locality Name (eg, city)
- Organization Name (eg, company)
- Organizational Unit Name (eg, section)
- Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname)
- Email Address
Above command generates two files under the current working directory, cert.pem and key.pem
Copy above files to /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/certs directory
1.2.4 Endpoints Configuration
RDA event gateway support below end point types.
- Syslog over TCP: Recieve syslog events over TCP protocol
- Syslog over UDP: Recieve syslog events over UDP protocol
- HTTP: Receive log events over HTTP protocol
- TCP: Receive log events over TCP protocol
- SNMP Traps: Receive SNMP traps over UDP protocol
- Filebeat: Receive log events over HTTP protocol from log shipping agents such as
filebeat&winlogbeat
Tip
In version 3.6.1 or above, the RDA Event Gateway agent introduces enhanced Syslog TCP/UDP endpoints, developed in Go (lang), to boost event processing rates significantly and optimize system resource utilization.
-
New Syslog TCP Endpoint Type: syslog_tcp_go
-
New Syslog UDP Endpoint Type: syslog_udp_go
Event gateway with the default configuration for each of the above end points as shown below. The endpoint configuration file is located @ /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/endpoint.yml
endpoints:
# Endpoint - Syslog Log events over TCP protocol
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: syslog_tcp_events
enabled: false
type: syslog_tcp
port: 5140
ssl: false
ssl_cert_dir: /certs
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: syslog_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: syslog_tcp_event_stream
# Endpoint - Syslog Log events over UDP protocol
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: syslog_udp_events
enabled: false
type: syslog_udp
port: 5141
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: syslog_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: syslog_udp_event_stream
# Endpoint - Events over HTTP protocol
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: http_events
enabled: false
type: http
ssl: false
ssl_cert_dir: /certs
content_type: auto
port: 5142
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: http_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: http_event_stream
# Endpoint - Events in JSON format over TCP protocol
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: tcp_json_events
enabled: false
type: tcp_json
ssl: false
ssl_cert_dir: /certs
port: 5143
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: tcp_json_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: tcp_json_event_stream
# Endpoint - Events from Filebeat agent
# type: filebeat - It is applicable for both Filebeat and Winlogbeat log shipping agents
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: filebeat_events # URL is implicit, http://ip:port/filebeat_events
type: filebeat
enabled: false
ssl: false
ssl_cert_dir: /certs
xpack_features: min
port: 5144
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: filebeat_log_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: filebeat_event_stream
# Endpoint - Windows log events from Winlogbeat agent
# type: filebeat - It is applicable for both Filebeat and Winlogbeat log shipping agents
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: winlogbeat_events # URL is implicit, http://ip:port/winlogbeat_events
type: filebeat
enabled: false
ssl: false
ssl_cert_dir: /certs
xpack_features: min
port: 5145
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: winlogbeat_log_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: winlogbeat_event_stream
# Endpoint - SNMP Traps over UDP protocol using go language
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each trap event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: snmp_trap_events
enabled: false
type: snmp_trap_go
port: 5146
community: cfxrda
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: snmp_trap_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: snmp_trap_event_stream
# Endpoint - SNMP Traps over UDP protocol using python
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each trap event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: snmp_trap_events
enabled: false
type: snmp_trap
port: 5147
community: cfxrda
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: snmp_trap_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: snmp_trap_event_stream
Note
As highlighted above to enable events make the particular enabled section as true
Info
For filebeat type endpoint, the supported version of the filebeat and winlogbeat log shipping agent is 7.8.1
1.2.4.1 Kafka Topic-Based Endpoint Configurations
Kafka is now supported from 1.4.0, endpoints need to be updated and changed, and go-based setup is required for all settings.
- Login to event gateway installed VM and edit the
endpoint.yamlfile as shown below
- name: snmp_trap_events
enabled: true
type: snmp_trap_go
port: 5146
community: cfxrda
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: snmp_trap_events_archive # Log archive name
##stream: "NULL"
##direct_to_stream: snmp_trap_event_stream
kafka:
- stream_name: trap_topic_kafka
context: external
retention.ms: "3600000"
- name: syslog_udp_events
enabled: true
type: syslog_udp_go
port: 5141
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: syslog_events_archive # Log archive name
##stream: "NULL"
##direct_to_stream: syslog_udp_go_event_stream
kafka:
- stream_name: syslog_topic_kafka
context: external
retention.ms: "3600000"
Creating Persistent Streams
- Login to the UI and Navigate as Follows
Navigation Path: Home -> RDA ADministration -> Persistent Streams -> Add -> Provide Pstream Name and Attributes as shown below and Click on Save
Pstream Name: trap_topic_kafka
Attributes
{
"retention_days": 2,
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"messaging_platform_settings": {
"platform": "kafka-external",
"kafka-params": {
"topics": [
"trap_topic_kafka"
],
"auto.offset.reset": "latest",
"consumer_poll_timeout": 1.0,
"batch_max_size": 1000,
"batch_max_time_seconds": 2
}
}
}
Pstream Name: syslog_topic_kafka
Attributes
{
"retention_days": 2,
"search_case_insensitive": true,
"messaging_platform_settings": {
"platform": "kafka-external",
"kafka-params": {
"topics": [
"syslog_topic_kafka"
],
"auto.offset.reset": "earliest",
"consumer_poll_timeout": 1.0,
"batch_max_size": 10000,
"batch_max_time_seconds": 1
}
}
}
1.2.5 Log Archival
Below document provides instructions on how to setup and configure Log Archiving feature in RDA Fabric platform.
1.2.5.1 About
Log Archival is a feature in the RDA Fabric platform that allows for the storage of all real-time ingested log messages or events for extended periods, ranging from 6 months to 1 year or more. These logs are stored in a compressed format at a rate of 80% to 90%.
The supported target is any S3 API compatible object storage.
As the first step, you need to configure a log archival repository that points to an S3 object storage endpoint. Each log archival repository may contain one or more named archives, which store the logs in a compressed format with minute-level granularity.
In addition, you need to configure the Event Gateway to save logs to one of the configured log archival repositories. Archived log data can be recalled or replayed at any time using RDA bots or the rdac command-line utility.
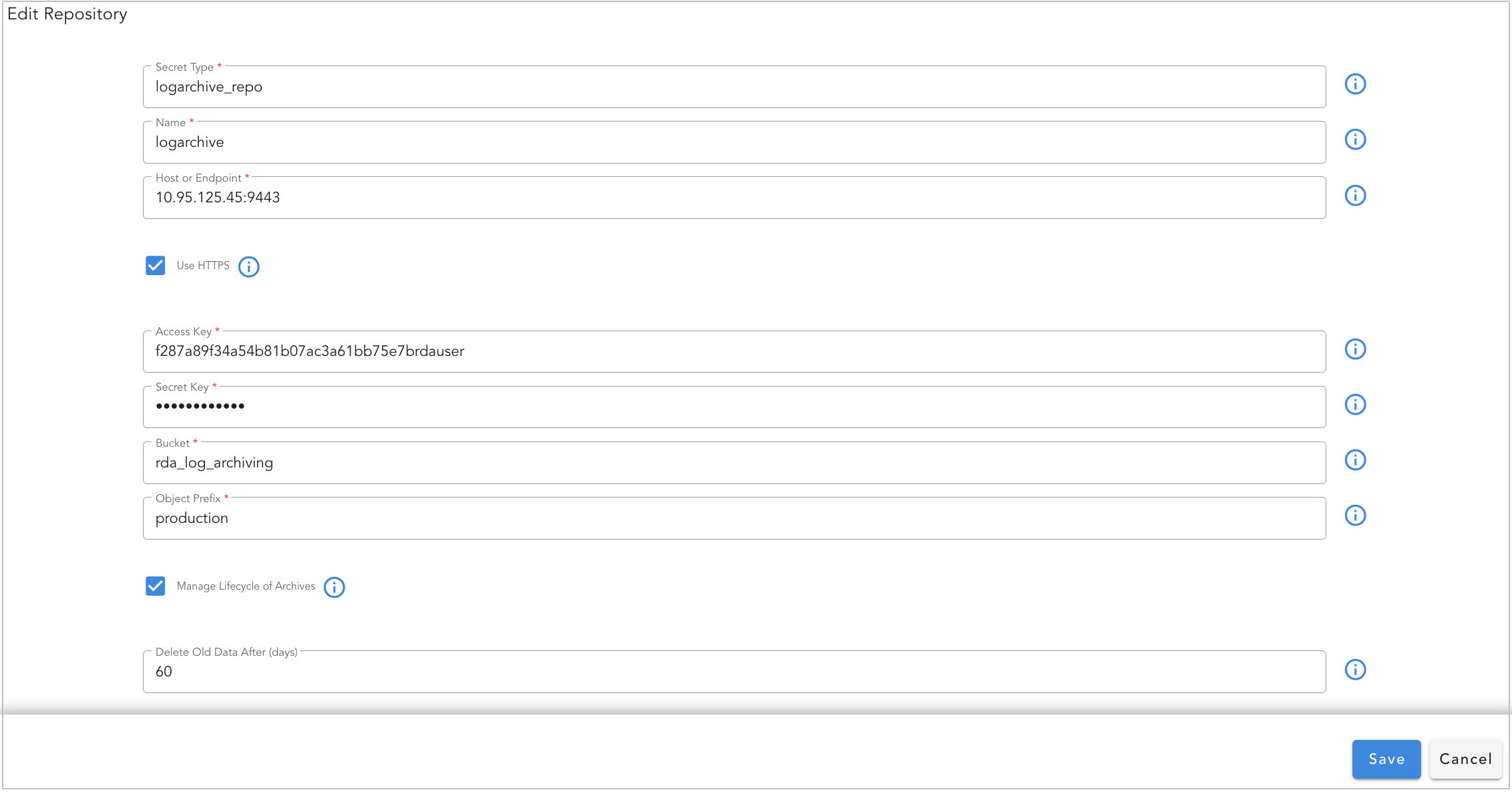
1.2.5.2 Add Log Archival Repository
Log archival repository can be configured through RDAF platform's UI portal or through rdac command-line utility.
Adding a Log Archival repository to utilize RDA Fabric platform's S3 storage using the rdac CLI.
Login as rdauser user into one of the RDA Fabric platform VMs using an SSH client (ex: putty) on which rdac CLI was installed.
Run the following rdac command to add a Log Archival repository and to utilize RDA Fabric platform's S3 object storage service.
--repo: Specify Log Archival repository name
--retention: Specify in number of days after which older Log Archival data to be deleted/purged
--prefix: Specify a prefix which can be used to identify archived logs (ex: production or stage etc)
Tip
Please note that when you add a Log Archival repository using the rdac CLI command to utilize RDA Fabric platform's S3 object storage service, it will automatically appear in the RDA Fabric's UI under Configuration → RDA Integrations → Log Archives
Adding a Log Archival repository using external S3 object storage in the RDA Fabric Portal through UI.
- Login into RDAF platform's UI portal
- Click on Configuration → RDA Integrations → Log Archives → Add Repository
Tip
Before configuring the log archival repository in the RDA Fabric platform, create an S3 bucket with read, write, and delete permissions on the target S3 object storage. This step is only necessary when external S3 object storage is being used.
Field Name |
Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name |
yes | Enter Log Archival repository name |
Host or Endpoint |
yes | S3 API compatible storage DNS Name or IP Address |
Use HTTPS |
no | Select this option to enable S3 APIs to be encrypted over HTTP protocol |
Access Key |
yes | Enter Access Key to access the configured S3 bucket for Log Archival repository |
Secret Key |
yes | Enter Secret Key to access the configured S3 bucket for Log Archival repository |
Bucket |
yes | Specify the S3 bucket name that is configured for Log Archival repository |
Object Prefix |
no | Specify a prefix which can be used to identify archived logs (ex: production or stage etc) |
Manage Lifecycle of Archives |
no | Select this option if the older Log Archival data to be deleted/purged after certain amount of time |
Delete Old Data After (days) |
no | Specify in number of days after which older Log Archival data to be deleted/purged |
1.2.5.3 Configure Log Archival Repository in Event Gateway
After configuring the Log Archival repository on RDA Fabric platform, Event Gateway need to be configured to utilize the configured repository to start archiving the ingested logs.
Log in as the rdauser user (or another configured user) to the machine where the RDA Event Gateway is installed using an SSH client (e.g., PuTTY).
- Update Event Gateway
serviceconfiguration:
Edit the Event Gateway's main configuration file /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/main/main.yml and enable Log Archival repository configuration as shown below.
# This is the main configuration for Event Gateway.
# Changes to this file only take affect after Event Gateway container restart
# Name of the site at which Even Gateway is deployed
# If not specified, uses ENV variable RDA_SITE_NAME. This option will override ENV variable value
site_name: event_gateway_site01
# Number of processes for publishing messages to RDA Stream. This will override ENV variable NUM_PROCESSES
num_procs: 1
...
...
# Log archival settings
archival:
enabled: true
# local directory where log files (JSONs and then .gz files) will be saved
local_dir: /tmp/log_archive/
# Name of the archival. Must be only letters and digits and optionally _-
name: "acme_log_archive"
# Local .gz files are deleted immediately after copying to destination (minio or s3)
# If not able to push to minio, how long to keep in local directory
local_retain_max_hours: 2
# Archival destination. If not specified, archival will be disabled
destination_repository: "logarchive_repo"
enabled: true to enable or false to disable Log Archival configuration
local_dir: default is set to /tmp/log_archive/. This path is used to temporarily store Log Archival data locally when the configured S3 object storage is inaccessible.
name: Specify Log Archival name
local_retain_max_hours: Specify number of hours to retain the Log Archival data locally when the configured S3 object storage is inaccessible. Local .gz files are deleted immediately after copying them to the repository on S3 object storage. Default value is 2 (hours)
destination_repository: Specify the Log Archival repository name that is configured in section 2.1
- Update Event Gateway
endpointconfiguration:
Log Archival is optional and it can be configured for each endpoint.
Edit Event Gateway's endpoint configuration file /opt/rdaf/event_gateway/config/endpoint.yml and configure the Log Archival for each endpoint.
Tip
The archive_name parameter is optional. When NOT configured for an endpoint, the Log Archive name that is configured in the Event Gateway's main.yml configuration file will be used.
endpoints:
# Endpoint - Syslog Log events over TCP protocol
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: syslog_tcp_events
enabled: true
type: syslog_tcp
port: 5140
ssl: false
ssl_cert_dir: /certs
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: syslog_tcp_log_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: syslog_tcp_event_stream
# Endpoint - Syslog Log events over UDP protocol
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: syslog_udp_events
enabled: true
type: syslog_udp
port: 5141
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: syslog_udp_log_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: syslog_udp_event_stream
archive_name: Specify the log archive name (optional).
Please restart the Event Gateway container after making the above changes.
Tip
Please check rda-event-gateway service logs to verify there are no configuration errors.
1.2.5.4 Log Archive Management using rdac CLI
rdac CLI supports Log Archival feature configuration and management using the below commands.
- Following are the available sub commands
Sub Commands |
Description |
|---|---|
| replay | Replay the data from given archive for a specified time interval with specified label |
| repos | List of all log archive repositories |
| add-platform | Add current platform Minio as logarchive repository |
| names | List archive names in a given repository |
| data-size | Show size of data available for given archive for a specified time interval |
| data-read | Read the data from given archive for a specified time interval |
| download | Download the data from given archive for a specified time interval |
| merge-files | Merge multiple locally downloaded Log Archive (.gz) filles into a single CSV/Parquet file |
Log Archive Replay: replay
It replays the archived log data from a given log archive name for a specified time interval.
Options:
--repo: Specify the Log Archival repository name
--name: Specify the Log Archival name for an endpoint
--from: Specify the start date and time from which log messages should be replayed. ISO datetime format is supported. (ex: 2023-10-29T20:45:24 or Oct 29 2023, 10am etc)
--to: Specify the end date and time up to which log messages should be replayed. ISO datetime format is supported. (ex: 2023-10-29T20:45:24 or Oct 29 2023, 10am etc)
--max_rows: Specify the maximum number of log messages to retrieve. When not specified, all log messages within the specified time duration will be replayed. (Optional)
--speed: Specify the log replay speed. 1 means close to the original speed. < 1 means slower than original. > 1 means faster than original. Please note that these speeds are approximate and cannot be guaranteed. 0 means no introduced latency, it will attempt to replay as fast as possible. (Optional) default value is set to 1
--batch_size: Specify the number of log messages to retrieve in each iteration. (Optional) default value is set to 100
--stream: Specify the stream name for ingesting the replayed log messages.
--label: Specify a custom label or name (e.g., 'production logs replay') to tag the replayed log messages. This label is useful for reporting and identifying different replay actions. (Optional)
--site: Specify the RDA Worker site name where the log replay job should be submitted.
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive replay command as an example.
rdac logarchive replay --repo logarchive \
--name syslog_tcp_log_archive \
--from 'Oct 29 2023, 10am' --to 'Oct 20 2023, 11.30pm' \
--max_rows 2 \
--stream syslog_tcp_event_stream_replay \
--site rda-site-01
@dm:logarchive-replay
repo = 'logarchive' &
archive = 'syslog_tcp_log_archive' &
from = '2023-10-29 10:00:00' &
minutes = -12240 &
to = '2023-10-20 22:00:00' &
label = 'Replay from CLI' &
max_rows = 2 &
speed = 0 &
batch_size = 100
--> @rn:write-stream name = 'syslog_tcp_event_stream_replay'
{
"status": "started",
"reason": "",
"now": "2023-10-29T21:07:00.412547",
"pipeline-name": "log_replay: Replay from CLI",
"status-subject": "tenants.032a23f3e54444f4b4e3ae69e7a3f5fb.worker.group.f4a56ba6388c.direct.45b07876",
"jobid": "8fd1d6109881409090fde448215002b3",
"attributes": {},
"pipeline-checksums": {
"log_replay: Replay from CLI": "9651d110"
}
}
Completed:
[
{
"archive_name": "syslog_tcp_log_archive",
"raw": "<14>1 2023-10-29T20:45:24.299351Z - - - - - \ufeff2023-10-29T20:45:24.299093+00:00 k8rdapfm01 kernel: [430992.418760] [UFW BLOCK] IN=tunl0 OUT=cali9e5fd88ad03 MAC= SRC=192.168.126.117 DST=192.168.110.222 LEN=112 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=62 ID=58098 DF PROTO=UDP SPT=50442 DPT=53 LEN=92 MARK=0x10000 ",
"rda_gw_client_ip": "192.168.125.45",
"rda_gw_ep_name": "syslog_tcp_events",
"rda_gw_ep_type": "syslog_tcp",
"rda_gw_timestamp": "2023-10-29T20:45:24.584935+00:00",
"rda_stream": "NULL",
"site_code": "event_gateway_site01",
"syslog_facility": "user",
"syslog_facility_num": 1,
"syslog_severity": "INFORMATIONAL",
"syslog_severity_num": 6
},
{
"archive_name": "syslog_tcp_log_archive",
"raw": "<14>1 2023-10-29T20:45:24.547496Z - - - - - \ufeff2023-10-29T20:45:24.547242+00:00 k8rdapfm01 systemd[1]: run-docker-runtime\\x2drunc-moby-e84a74691b038cbc0729e2f689b2dd2bc5f12636555c68aad763d5c6e977b54f-runc.dLNMgh.mount: Succeeded.",
"rda_gw_client_ip": "192.168.125.45",
"rda_gw_ep_name": "syslog_tcp_events",
"rda_gw_ep_type": "syslog_tcp",
"rda_gw_timestamp": "2023-10-29T20:45:24.595768+00:00",
"rda_stream": "NULL",
"site_code": "event_gateway_site01",
"syslog_facility": "user",
"syslog_facility_num": 1,
"syslog_severity": "INFORMATIONAL",
"syslog_severity_num": 6
}
]
Add Log Archive Repositories: add-platform
It adds RDA platform's S3 object storage service (Minio) as a logarchive repository
Options:
--repo: Specify Log Archival repository name
--retention: Specify in number of days after which older Log Archival data to be deleted/purged
--prefix: Specify a prefix which can be used to identify archived logs (ex: production or stage etc)
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive add-platform command as an example.
List Log Archive Repositories: repo
It lists all configured log archive repositories
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive repos command as an example.
[
{
"name": "demo_logarchive",
"endpoint": "192.168.125.11:9443",
"bucket": "tenants.a7bdea6599b44623b230f69526e9d543",
"object_prefix": "demo_logs/"
},
{
"name": "logsrepo",
"endpoint": "s3.isv.scality.com",
"bucket": "cfx-125-11",
"object_prefix": "/"
},
{
"name": "platform_repo",
"endpoint": "192.168.125.11:9443",
"bucket": "tenants.a7bdea6599b44623b230f69526e9d543",
"object_prefix": "demo"
}
]
List Log Archives with a Repository: names
It lists log archive names in a given log archival repository.
Options:
--repo: Specify Log Archival repository name
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive names command as an example.
[
{
"arhive_name": "sythentic-syslogs",
"num_days": 275,
"first_day": "2022/12/06",
"last_day": "2023/10/04"
}
]
List Log Archives Data Size: data-size
It shows the size of data (in bytes) available for given log archive for a specified time interval
Options:
--repo: Specify Log Archival repository name
--name: Specify the Log Archival name for an endpoint
--from: Specify the start date and time from which log messages should be replayed. ISO datetime format is supported. (ex: 2023-10-29T20:45:24 or Oct 29 2023, 10am etc)
--minutes: Specify the time in minutes relative to the date and time specified in the --from option.
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive data-size command as an example.
rdac logarchive data-size --repo logarchive \
--name syslog_events_archive \
--from 'Oct 10 2023, 10am' --minutes 30
+---------------------+-------------------+------------------------+
| Timestamp | Number of Files | Compressed Data Size |
|---------------------+-------------------+------------------------|
| 2023-10-10T10:00:00 | 1 | 22,441 |
| 2023-10-10T10:01:00 | 1 | 21,588 |
| 2023-10-10T10:02:00 | 1 | 19,009 |
| 2023-10-10T10:03:00 | 1 | 24,985 |
...
...
| 2023-10-10T10:27:00 | 1 | 18,662 |
| 2023-10-10T10:28:00 | 1 | 19,322 |
| 2023-10-10T10:29:00 | 1 | 21,968 |
| 2023-10-10T10:30:00 | 1 | 20,764 |
| TOTAL | 31 | 650,720 |
+---------------------+-------------------+------------------------+
Read Data from Log Archive: data-read
It reads the data from a given log archive for a specified time interval and prints the output on the console.
Options:
--repo: Specify Log Archival repository name
--name: Specify the Log Archival name for an endpoint
--from: Specify the start date and time from which log messages should be replayed. ISO datetime format is supported. (ex: 2023-10-29T20:45:24 or Oct 29 2023, 10am etc)
--minutes: Specify the time in minutes relative to the date and time specified in the --from option.
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive data-read command as an example.
rdac logarchive data-read --repo logarchive \
--name syslog_events_archive \
--from 'Oct 10 2023, 10am' \
--minutes 30 \
--max_rows 2
[
{
"rda_gw_ep_type": "syslog_udp",
"rda_gw_seq": 3666473,
"raw": "<163>2023-10-10T10:00:00.318Z R810-dev-2.engr.cloudfabrix.com Hostd: error hostd[36F40B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Default opID=0778c9cb] Unable to convert Vigor value 'centos8-64' of type 'char const*' to VIM type 'Vim::Vm::GuestOsDescriptor::GuestOsIdentifier'\n",
"rda_gw_client_ip": "192.168.158.210",
"rda_gw_ep_name": "syslog_udp_events",
"rda_gw_timestamp": "2023-10-10T10:00:00.349091+00:00",
"rda_stream": "syslog_udp_event_stream",
"syslog_facility": "local4",
"syslog_facility_num": 20,
"syslog_severity": "ERROR",
"syslog_severity_num": 3,
"site_code": "event_gateway_site01",
"archive_name": "syslog_events_archive"
},
{
"rda_gw_ep_type": "syslog_udp",
"rda_gw_seq": 3666474,
"raw": "<163>2023-10-10T10:00:00.319Z R810-dev-2.engr.cloudfabrix.com Hostd: error hostd[36840B70] [Originator@6876 sub=Default opID=0778c9ca] Unable to convert Vigor value 'centos8-64' of type 'char const*' to VIM type 'Vim::Vm::GuestOsDescriptor::GuestOsIdentifier'\n",
"rda_gw_client_ip": "192.168.158.210",
"rda_gw_ep_name": "syslog_udp_events",
"rda_gw_timestamp": "2023-10-10T10:00:00.349602+00:00",
"rda_stream": "syslog_udp_event_stream",
"syslog_facility": "local4",
"syslog_facility_num": 20,
"syslog_severity": "ERROR",
"syslog_severity_num": 3,
"site_code": "event_gateway_site01",
"archive_name": "syslog_events_archive"
},
]
Download Log Data from Log Archive: download
It downloads the compressed log data (.gz) files from given log archive for a specified time interval.
Options:
--repo: Specify Log Archival repository name
--name: Specify the Log Archival name for an endpoint
--from: Specify the start date and time from which log messages should be replayed. ISO datetime format is supported. (ex: 2023-10-29T20:45:24 or Oct 29 2023, 10am etc)
--minutes: Specify the time in minutes relative to the date and time specified in the --from option.
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive download command as an example.
rdac logarchive download --repo logarchive --name syslog_events_archive \
--from 'Oct 10 2023, 10am' \
--minutes 1440 \
--out ./log_archive_download
Downloaded object /syslog_events_archive/2023/10/10/10/00/2d2b42a9.gz
Downloaded object /syslog_events_archive/2023/10/10/10/01/2d2b42a9.gz
Downloaded object /syslog_events_archive/2023/10/10/10/02/2d2b42a9.gz
Downloaded object /syslog_events_archive/2023/10/10/10/03/2d2b42a9.gz
...
Downloaded object /syslog_events_archive/2023/10/10/10/14/2d2b42a9.gz
Downloaded object /syslog_events_archive/2023/10/10/10/15/2d2b42a9.gz
Merge Log Data files: merge-files
It merges multiple locally downloaded Log Archive (.gz) filles into a single CSV/Parquet file.
Please refer to the below rdac logarchive merge-files command as an example.
rdac logarchive merge-files --folder ./log_archive_download/syslog_events_archive/2023/10/25/10/10/ \
--tofile ./log_archive_download/log_archive_merge.csv
Total rows in final dataframe: 1
{
"mem_total_gb": 47.034,
"mem_available_gb": 26.113,
"mem_percent": 44.5,
"mem_used_gb": 19.703,
"mem_free_gb": 1.327
}
Saving CSV file: /logarchive
1.2.5.5 Log Archive Replay
Archived log messages can be replayed on-demand as per user's requirement either using rdac logarchive CLI or through RDA Fabric platform's UI portal.
Tip
For log messages replay using rdac logarchive CLI, please refer Log Archival Management using rdac CLI section.
The steps below outline how to replay log messages from the RDA Fabric platform's UI portal.
1. Login into UI portal and go to Main Menu --> Configuration --> RDA Integrations --> Log Archives --> Click on Log Archive Repository --> Select one of the Log Archive name and click on Replay
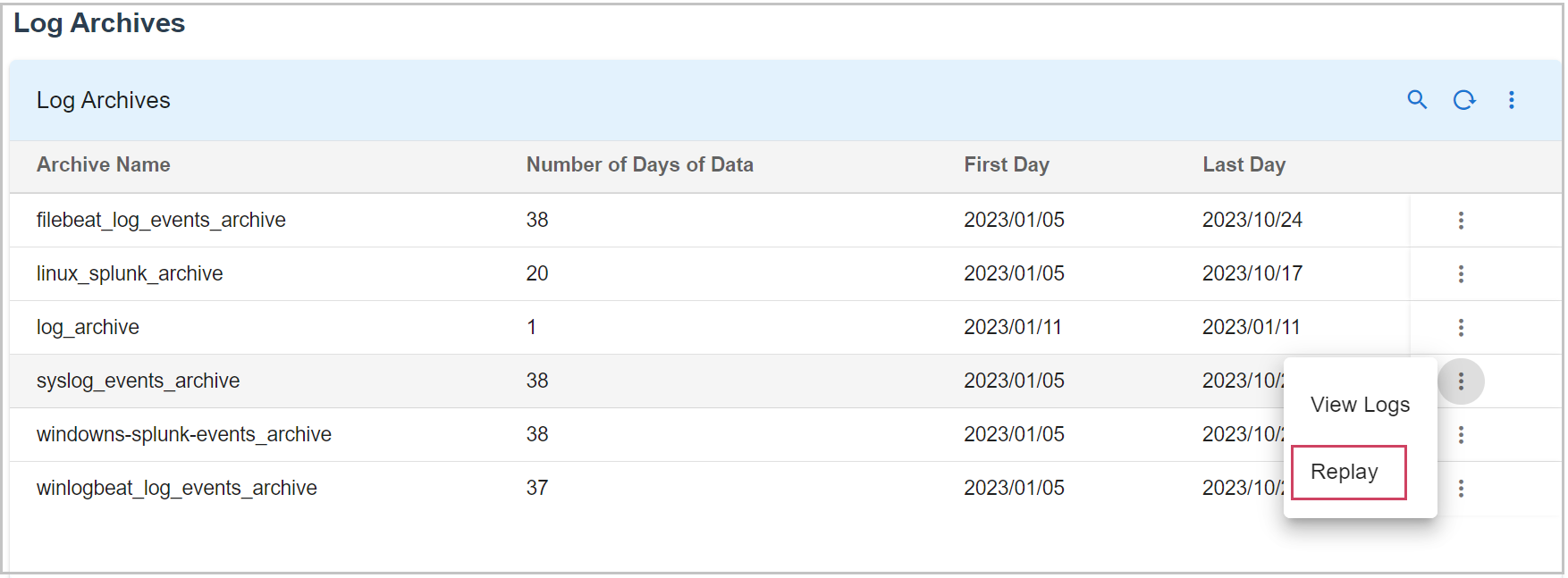
2. After Clicking on Replay you need to give the UTC Timeslot of your required logs to replay as shown below in the Screenshot
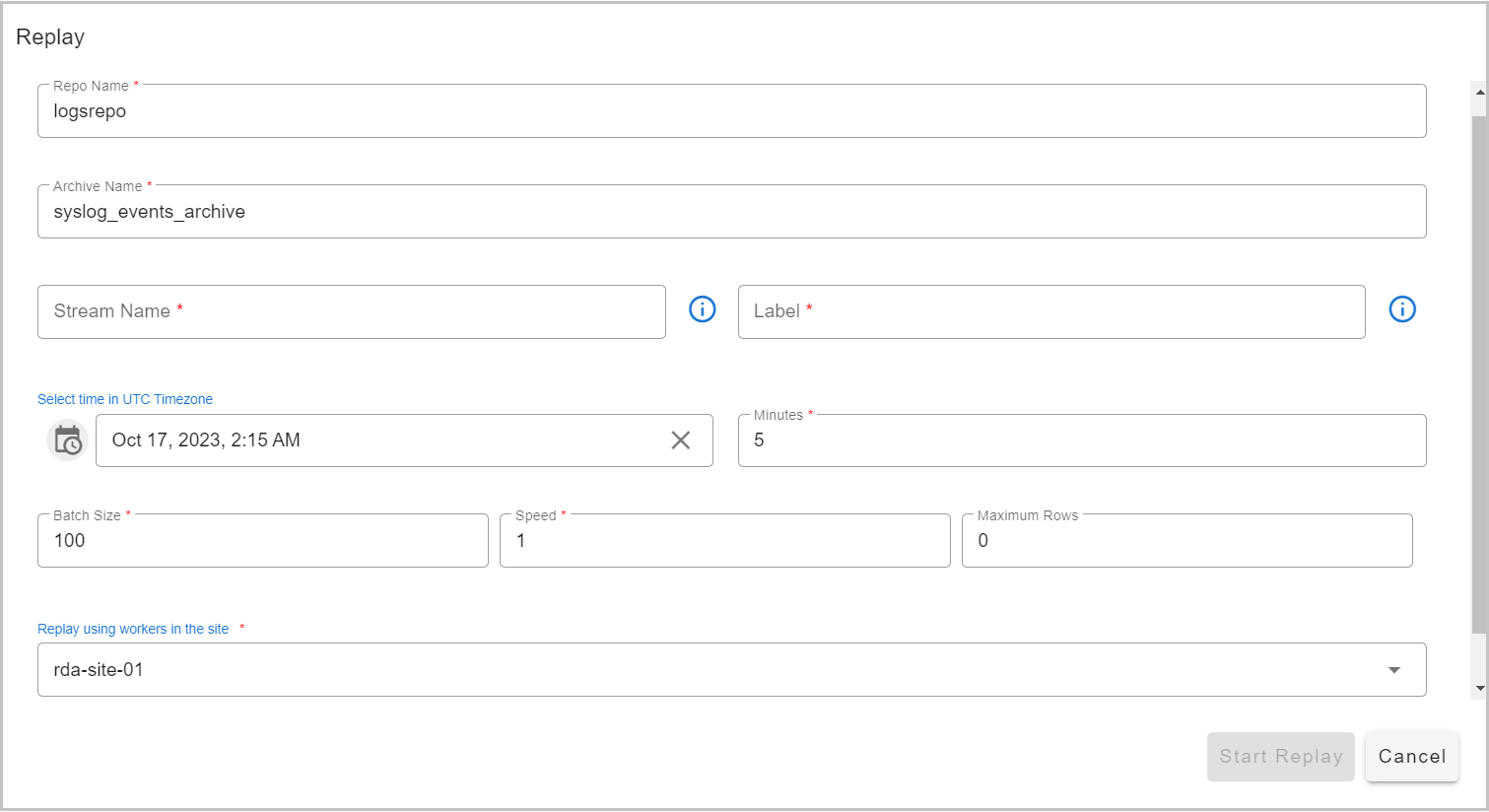
Note
Specify the stream name for ingesting the replayed log messages. Specify Label name (e.g., 'production logs replay') to tag the replayed log messages. This label is useful for reporting and identifying different replay actions.
1.2.5.6 Log Archive Bots
RDA Fabric platform also provides logarchive bots which can be used in RDA pipelines. Below screenshot shows the available logarchive bots.

- The following pipeline provides an example on how to use
logarchive-replaybot within a RDA pipeline.
@dm:logarchive-replay repo = "logarchive_repo" and
archive = 'syslog_tcp_log_archive' and
from = "2023-10-26 17:24:14" and
minutes = 30 and
batch_size = 100
--> @rn:write-stream name = 'logarchive_replay_stream'
[
{
"archive_name": "syslog_tcp_log_archive",
"raw": "<14>1 2023-10-29T20:45:24.299351Z - - - - - \ufeff2023-10-29T20:45:24.299093+00:00 k8rdapfm01 kernel: [430992.418760] [UFW BLOCK] IN=tunl0 OUT=cali9e5fd88ad03 MAC= SRC=192.168.126.117 DST=192.168.110.222 LEN=112 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=62 ID=58098 DF PROTO=UDP SPT=50442 DPT=53 LEN=92 MARK=0x10000 ",
"rda_gw_client_ip": "192.168.125.45",
"rda_gw_ep_name": "syslog_tcp_events",
"rda_gw_ep_type": "syslog_tcp",
"rda_gw_timestamp": "2023-10-29T20:45:24.584935+00:00",
"rda_stream": "NULL",
"site_code": "event_gateway_site01",
"syslog_facility": "user",
"syslog_facility_num": 1,
"syslog_severity": "INFORMATIONAL",
"syslog_severity_num": 6
},
{
"archive_name": "syslog_tcp_log_archive",
"raw": "<14>1 2023-10-29T20:45:24.547496Z - - - - - \ufeff2023-10-29T20:45:24.547242+00:00 k8rdapfm01 systemd[1]: run-docker-runtime\\x2drunc-moby-e84a74691b038cbc0729e2f689b2dd2bc5f12636555c68aad763d5c6e977b54f-runc.dLNMgh.mount: Succeeded.",
"rda_gw_client_ip": "192.168.125.45",
"rda_gw_ep_name": "syslog_tcp_events",
"rda_gw_ep_type": "syslog_tcp",
"rda_gw_timestamp": "2023-10-29T20:45:24.595768+00:00",
"rda_stream": "NULL",
"site_code": "event_gateway_site01",
"syslog_facility": "user",
"syslog_facility_num": 1,
"syslog_severity": "INFORMATIONAL",
"syslog_severity_num": 6
}
]
1.2.6 Adding Addtional Attributes
1. How to add additional attribute to EG in the endpoint.yml file
Attributes
-
site_code:
event_gateway_site01# Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed -
archive_name:
syslog_events_archive# Log archive name -
event_gateway_name: EG01 # make it unique for each EG deployed in HA setup
2. Add netstat checks to make sure endpoint enabled ports are visible at the VM level
3. Once the RDA backend is up and running, validate that messages are coming from all event gateways by looking at event_gateway_name value in the data stream
1.2.7 RDA Event Gateway Upgrade Steps
Tip
For latest version of RDA Event Gateway agent, please refer release notes.
Step-1: Login to the RDA Event Gateway agent installed VM
Step-2: Navigate to the directory location where RDA Event Gateway agent was installed.
Step-3: Edit the docker-compose file for the RDA Event Gateway.
Edit and update the RDA Event Gateway agent tag (e.g., from 3.4.2.1 to 3.6.1) as shown below.
Step-4: Save and Exit
Step-5: Run the following commands to upgrade the RDA Event Gateway agent. (Note: Use the appropriate docker-compose filename if it differs from the one mentioned below.)
docker-compose -f event-gateway-docker-compose.yml down
docker-compose -f event-gateway-docker-compose.yml pull
docker-compose -f event-gateway-docker-compose.yml up -d
Step-6: Use the docker ps -a command as shown below to ensure that the RDA Event Gateway agent is up and running.
b6861c4f79b5 docker1.cloudfabrix.io:443/external/ubuntu-rda-event-gateway:8.0.0 "/bin/bash -c 'cd /o…" 1 minutes ago Up 1 minutes deployment-scripts-rda_event_gateway-1
Tip
In version 3.6.1 or above, the RDA Event Gateway agent introduces enhanced Syslog TCP/UDP endpoints, developed in Go (lang), to boost event processing rates significantly and optimize system resource utilization.
-
New Syslog TCP Endpoint Type: syslog_tcp_go
-
New Syslog UDP Endpoint Type: syslog_udp_go
To use syslog_tcp_go, syslog_udp_go, or both, please follow the steps below.
Note
Before updating, take a backup of endpoint.yml. If there are two Event Gateways, make a backup from each one.
Edit endpoint.yaml using the below mentioned command
-
Change type:syslog_udp to type:syslog_udp_go
-
Change type:syslog_tcp to type:syslog_tcp_go
- name: syslog_tcp_events
enabled: true
type: syslog_tcp_go
port: 5140
ssl: false
ssl_cert_dir: /certs
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: syslog_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: syslog_tcp_event_stream
# Endpoint - Syslog Log events over UDP protocol
# attrs: <Custom attributes to be added for each log event, provide one or more attributes in key: value format>
# stream: <Write the log events to a Stream within RDA Fabric>
- name: syslog_udp_events
enabled: true
type: syslog_udp_go
port: 5141
attrs:
site_code: event_gateway_site01 # Site Name / Code where Event gateway is deployed
archive_name: syslog_events_archive # Log archive name
stream: "NULL"
direct_to_stream: syslog_udp_event_stream
- Restart the RDA Event Gateway Agent
Run the command below to get the RDA Event Gateway agent container ID.
Run the command below to restart the RDA Event Gateway agent container.
Please wait for 30 seconds and use the command below to check RDA Event Gateway agent logs for any errors
1.4 RDA Edge Collector Installation
Note
Edge Collector or Edge Collector Agent wherever mentioned below in the Document refers to same component.
Prerequisites:
- Linux OS
- Memory - 8GB
- Disk - 50GB
- Python 3.7.4 or above
-
Docker Version (18.09.2 or above)
-
Docker Compose (1.27.x and above)
Installation Steps:
Step-1:
The RDA Edge Collector agent registers and communicates with the RDAF platform using a configuration file that contains your tenant ID, data fabric access tokens, and object storage credentials.
Download RDA Fabric Configuration from the portal by going to Configuration --> RDA Administration --> Network and copy it to the local filesystem where the edge collector agent is going to be installed.
- Save the file as
rda_network_config.json

- Create the below directory structure
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/network_config
sudo mkdir -p /opt/rdaf/edgecollector/cred
sudo chown -R `id -u`:`id -g` /opt/rdaf
- Copy the downloaded RDA Fabric configuration file as shown below.
Step-2: Docker Login
Run the below command to create and save the docker login session into CloudFabrix's secure docker repository.
Step-3: Create Docker Compose File
Create docker compose configuration file for RDA Edge Collector as shown below.
Tip
Note-1: Optionally change the edge collector's group name (also known as Site) in the docker-compose file by updating the agent-group-name value. In this example, the edge collector's group name is specified as ec-group-01
Note-2: Adjust mem_limit and memswap_limit as per the workload requirements. In the below configuration, these parameters are set to 6GB
cd /opt/rdaf/edgecollector
cat > rda-edgecollector-docker-compose.yml <<EOF
version: '3.1'
services:
rda_edgecollector_agent:
image: 'cfxregistry.cloudfabrix.io/cfxcollector:daily'
container_name: rda_edgecollector_agent
restart: always
network_mode: host
mem_limit: 6G
memswap_limit: 6G
volumes:
- /opt/rdaf/network_config:/network_config
- /opt/rdaf/edgecollector:/cfxedgecollector
- /opt/rdaf/edgecollector/cred:/cred
environment:
RDA_NETWORK_CONFIG: /network_config/rda_network_config.json
PYTHONPATH: /opt/cfx-rda-edgeagent
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "25m"
max-file: "5"
ulimits:
nproc:
soft: 64000
hard: 128000
nofile:
soft: 64000
hard: 128000
entrypoint:
- /bin/bash
- '-c'
- >-
cd /opt/cfx-rda-edgeagent/src/; python -c 'import edgecollector_rda_agent ;
edgecollector_rda_agent.run()' --creddir /cred/ --agent-group-name ec-group-01
EOF
cd /opt/rdaf/edgecollector
docker-compose -f rda-edgecollector-docker-compose.yml pull
docker-compose -f rda-edgecollector-docker-compose.yml up -d
Step-5: Check Edge Collector Status
Check Edge Collector agent status using docker ps command and ensure that it is up and running, without any restarts. If you see that if it is restarting, make sure you copied the RDA network config file to the correct location.
Step-6: Verify RDA Edge Collector in RDA Fabric portal
A newly installed Edge Collector will authenticate with the RDA Fabric platform and it will show up in RDA Fabric portal under Fabric Health --> Agents .
Step-7: Verify Edge Collector using RDA Client (rdac) utility
If you have installed RDA Client (rdac) command line utility, you can also verify newly created Edge Collector using rdac agents command.
1.4.1 RDA Edge Collector Upgrade Steps
Step-1: Login to the EC agent installed VM
Step-2: Navigate to the location where EC agent was previously installed. see the example below.
Step-3: Edit the docker-compose file for the EC agent using a local editor (e.g. vi).
Edit and update EC agent tag – Tag x → Tag 3.7.2Step-4: Save and Exit
Step-5: Please run the following commands
docker-compose -f < docker-compose file name> down
docker-compose -f < docker-compose file name> pull
docker-compose -f < docker-compose file name> up -d
Step-6: Use the docker ps -a command as shown below to ensure that the RDA docker instances are up and running.